Setting up Snowflake to use Git¶
When you connect your Snowflake account to a remote Git repository, Snowflake creates a Git repository clone, copying the latest version of all files in the repository (a shallow clone) and storing metadata about the location of the remote repository, credentials (if needed), and configuration details about how Snowflake should interact with the Git repository API.
Depending on your requirements, by configuring components for authentication, interaction with the Git API, and communication over a private link between Snowflake and your cloud service provider, you can set up Snowflake so that a remote Git repository becomes an integral part of your workflow within Snowflake.
Choose a configuration model¶
Depending on your network and workflow requirements, you can configure Snowflake for access to a remote Git repository in any of several ways. The following lists example use cases, along with the repository access strategies you might use to support them.
Work with files on a Git repository through a workflow that includes pulling, pushing, and creating files.
When using Snowflake Workspaces, you can configure an API Integration for OAuth2 to simplify user authentication to Git repositories.
Reference files on a Git repository as part of a data pipeline or ML project.
If a scripted process will access the repository, consider authenticating using a token.
Get started by cloning a public repository (including Snowflake Labs) to run SQL scripts or notebook files in Snowflake Workspaces.
You can use Workspaces for
.sqlfiles, Snowflake notebooks for.ipynbfiles, or Snowflake Workspaces for.pyfiles.
The following describes options in terms of whether you want access over a public network or a private network:
Access over a public network |
Access over a private network |
|---|---|
Access over a public network allows you to authenticate to your remote Git repository server using the entire IP range of your Snowflake cloud provider deployment (because Snowflake does not provide a static IP range).
|
Access over a private network helps you avoid allowing access to the Git server for the entire IP range of your Snowflake cloud provider deployment. You can configure Snowflake to establish outbound connectivity through an outbound private link connection between Snowflake and your cloud infrastructure. Snowflake routes Git traffic through this connection to the Git repository server.
|
Configure Snowflake for access over a public network¶
You can set up Snowflake to access your Git repository over a public network. You can have Snowflake authenticate using any of the following strategies:
-
Configure an API integration with details about the Git repository server.
Authenticate with a token, such as a personal access token.
Configure a secret containing the username and token to use, then configure an API integration that allows Snowflake to use the secret when authenticating.
Authenticate through an OAuth flow.
Configure an API integration to allow for an OAuth2 flow.
Configure for no authentication¶
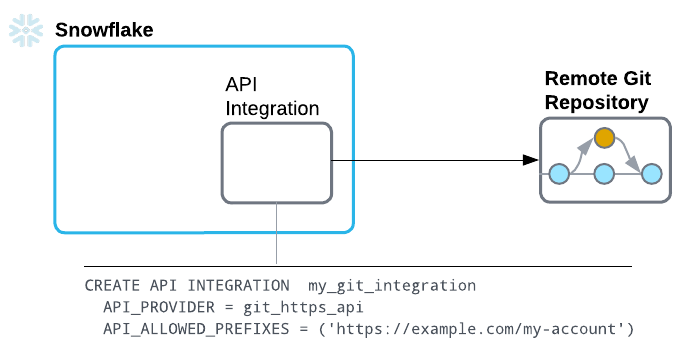
To set up Snowflake to use a Git repository without authenticating, follow these steps:
Create an API integration that supports access without authenticating, and specify the following details:
git_https_apias the value of the API_PROVIDER parameterHTTPS endpoints to which requests must be limited as values of the API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES parameter
For more information, see CREATE API INTEGRATION.
CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://example.com/my-account') ENABLED = TRUE;
Create a Git repository clone as described in Create a Snowflake Git repository clone.
Configure for authenticating with a token¶
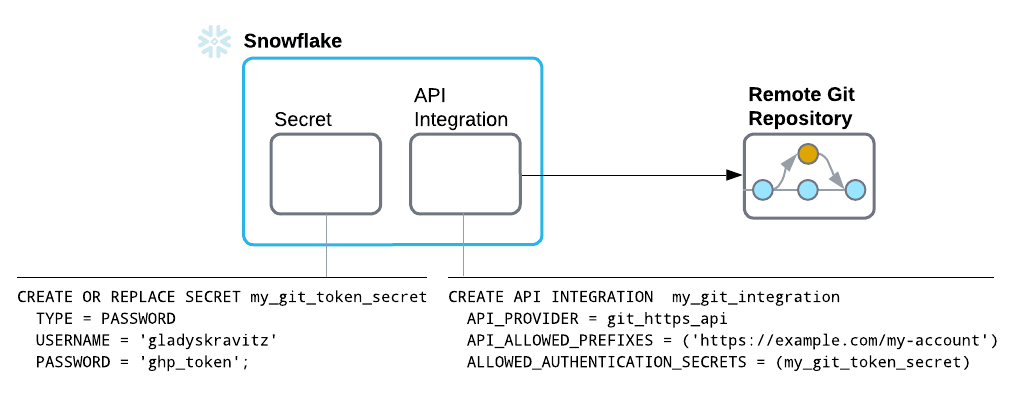
To have Snowflake authenticate with the Git repository by using a username and token such as a personal access token (PAT), follow these steps:
Provide credentials in a basic authentication secret.
To provide the credentials that Snowflake uses to authenticate with the repository, create a secret that contains the following:
A TYPE value of
passwordA username and token, such as a personal access token (PAT)
If your Git repository is hosted on Bitbucket, specify
x-token-authas the username value.Note
For information about creating a personal access token in GitHub, see Managing your personal access tokens in the GitHub documentation.
For more information on the SQL command for creating a secret, see the CREATE SECRET.
Code in the following example creates a secret called
my_git_secretwith a username and the user’s personal access token to use as credentials:CREATE OR REPLACE SECRET db.schema.my_git_secret TYPE = password USERNAME = 'gladyskravitz' PASSWORD = 'ghp_token';
Create an API integration that supports authenticating with a token.
To create an API integration for access to a Git repository without authenticating, specify the following details:
git_https_apias the value of the API_PROVIDER parameterHTTPS endpoints to which requests must be limited as values of the API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES parameter
For more information, see CREATE API INTEGRATION.
CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://github.com/my-account') ALLOWED_AUTHENTICATION_SECRETS = (my_git_secret) ENABLED = TRUE;
Create a Git repository clone as described in Create a Snowflake Git repository clone.
Configure for authenticating with OAuth¶
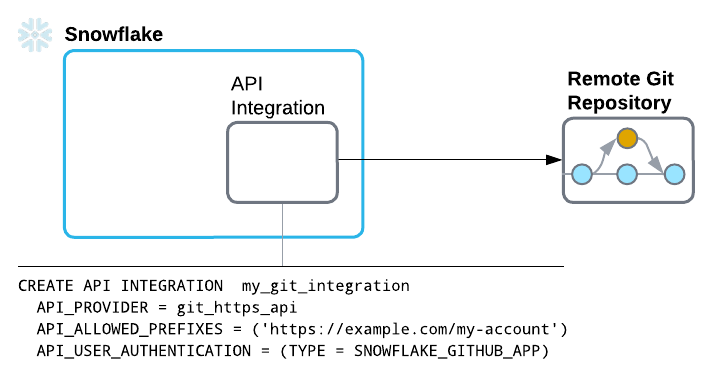
You can configure Snowflake to authenticate with the remote Git repository using an OAuth2 flow. How you set up for OAuth2 authentication differs depending on the repository provider.
If you’re using GitHub, you can create an API integration that uses the Snowflake GitHub App to authenticate.
The Snowflake GitHub App is a pre-configured OAuth2 application used by Snowflake and designed to simplify authentication. You don’t need to configure this app; you only need to create an API integration that specifies the Snowflake GitHub App.
For all repository providers, including GitHub, you can instead create an API integration that specifies values for OAuth2 parameters, including the client ID and secret, to use when authenticating.
Before you create the API integration, collect OAuth2 parameters for your repository provider, including the client ID and secret. You’ll specify these values in the API integration.
For more information, see the repository provider’s documentation.
To set up Snowflake so that it authenticates with the remote Git repository using an OAuth2 flow, follow these steps:
Create an API integration that supports authenticating through OAuth2.
Create an API integration that specifies the following values:
An API_PROVIDER parameter value of
git_https_apiAn API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES parameter value that specifies the HTTPS endpoints to which requests must be limited
An API_USER_AUTHENTICATION value that corresponds to the Git repository provider you’re using
When authenticating with GitHub using the Snowflake GitHub App, specify
(TYPE = SNOWFLAKE_GITHUB_APP).When authenticating with a repository provider without using the Snowflake GitHub App — such as with any repository provider other than GitHub — specify values for the following parameters, as described in CREATE API INTEGRATION:
OAUTH_CLIENT_ID
OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET
API_USER_AUTHENTICATION
OAUTH_AUTHORIZATION_ENDPOINT
OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT
OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDITY
OAUTH_REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDITY
OAUTH_ALLOWED_SCOPES
Code in the following examples creates an API integration called
my_git_api_integration:CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://github.com') API_USER_AUTHENTICATION = (TYPE = SNOWFLAKE_GITHUB_APP) ENABLED = TRUE;
CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://example.com/my_account') API_USER_AUTHENTICATION = ( TYPE = OAUTH2 OAUTH_AUTHORIZATION_ENDPOINT = '<your_oauth_authorization_endpoint>' OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT = '<your_oauth_token_endpoint>' OAUTH_CLIENT_ID = '<your_oauth_client_id>' OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET = '<your_oauth_client_secret>' OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDITY = 3600 OAUTH_REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDITY = 2592000 OAUTH_ALLOWED_SCOPES = ( 'read_api', 'read_repository', 'write_repository' ) ) ENABLED = TRUE;
Create a workspace connected to a Git repository as described in Create a Git workspace.
Configure Snowflake for access over a private network¶
You can configure Snowflake to establish outbound connectivity through an outbound private link connection between Snowflake and your cloud infrastructure. Snowflake routes Git traffic through this connection to the Git repository server.
With a private link connection, you avoid allowing access to the Git server for the entire IP range of your Snowflake cloud provider deployment. This section describes the steps at a high level.
Configure the private link connection.
You’ll apply configuration changes to both Snowflake and your cloud service infrastructure. This topic describes the steps on the Snowflake side. For details about all the steps, including about configuring your cloud service provider, see the knowledge base article Configuring Git Integration with Snowflake over Private Link.
Note
Snowflake supports only connections within the same cloud and region. For example, if your Snowflake deployment is on AWS in the us-west-2 region, then your other components must also be in that region.
Configure the private link connection¶
Before you can configure Snowflake for access to the remote Git repository, you must set up a private link between Snowflake and your cloud service provider.
To apply configuration changes to both Snowflake and your infrastructure, follow these steps:
In your cloud service provider, create a private link service to receive requests from the Snowflake private endpoint service.
For details, see the knowledge base article Configuring Git Integration with Snowflake over Private Link.
In Snowflake, provision a private endpoint that will reach your infrastructure through a private IP.
To provision the endpoint, use the SYSTEM$PROVISION_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT function with the following two arguments:
Your cloud provider’s private link service ID
Your Git server’s domain name
SELECT SYSTEM$PROVISION_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT( 'com.amazonaws.vpce.us-west-2.vpce-svc-xxx', // VPC Endpoint Service Name 'git_address.com' // Git server domain );
SELECT SYSTEM$PROVISION_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT( '/subscriptions/9217bbdd-434e-4dbb-97c2-0825c627a277/resourceGroups/git-server_group/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateLinkServices/git-server-pl-service', // Private Service ID 'git_address.com' // Git server domain );
SELECT SYSTEM$PROVISION_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT( 'projects/my-google-project/regions/us-east4/serviceAttachments/gitservice', // Service attachement field 'git_address.com' // Git server domain );
In your cloud service provider, accept the Snowflake private endpoint setup to finish setting up the private link connection.
To check status of the provisioning, call the SYSTEM$GET_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINTS_INFO system function.
Configure Snowflake access to the remote Git repository¶
After you set up a private link between Snowflake and your cloud service provider, you can configure Snowflake access to the remote Git repository.
Create an API integration that supports authenticating with a certificate.
Because Snowflake will reach your Git server using the HTTPS protocol, the domain name needs to have a valid certificate. The configuration you use differs depending on whether you use a self-signed certificate or a certificate signed by a certificate authority.
Using a self-signed certificate:
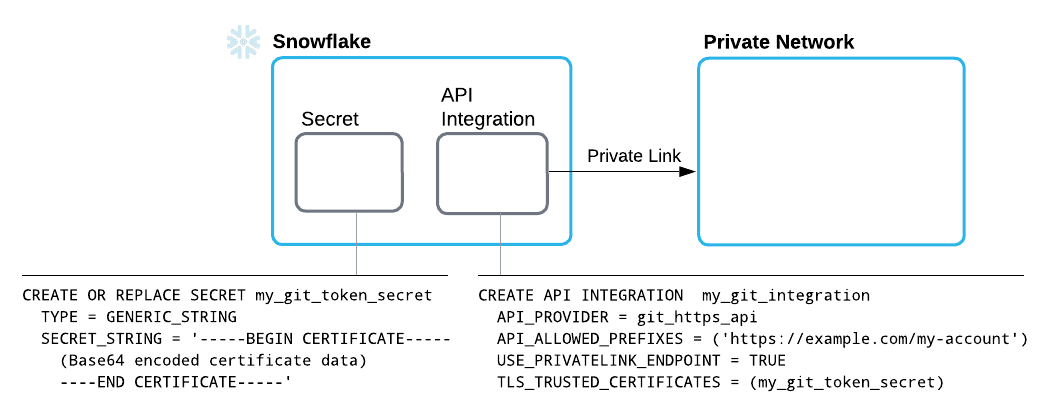
Provide credentials in a generic string secret.
This should be a public key of a self-signed domain to establish an HTTPS connection. To provide to Snowflake the credentials it will use to authenticate with the server, create a secret that contains the following details:
A TYPE parameter value of
GENERIC_STRINGA public certificate string as the value of the SECRET_STRING parameter
For the parameter’s value, specify a secret string, such as a public certificate body.
CREATE OR REPLACE SECRET my_public_certificate TYPE = GENERIC_STRING SECRET_STRING = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <certificate_body> -----END CERTIFICATE-----';
Create an API integration to integrate with the Git API, and specify the following details:
An API_PROVIDER parameter set to
git_https_apiAn API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES set to the base URL beneath which access is allowed
A USE_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT parameter set to
TRUEA TLS_TRUSTED_CERTIFICATES parameter set to the name of the secret you created, which contains the certificate
For more information, see CREATE API INTEGRATION.
CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://example.com/my-account') ALLOWED_AUTHENTICATION_SECRETS = ALL USE_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT = TRUE TLS_TRUSTED_CERTIFICATES = (my_public_certificate) ENABLED = TRUE;
Using a certificate signed by a certificate authority:
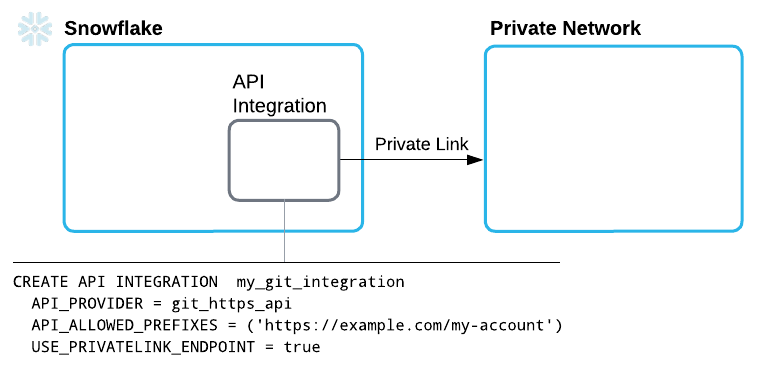
Create an API integration to integrate with the Git API, and specify the following details:
An API_PROVIDER parameter set to
git_https_apiAn API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES set to the base URL beneath which access is allowed
A USE_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT parameter set to
TRUEA TLS_TRUSTED_CERTIFICATES parameter set to the name of the secret you created, which contains the certificate
For more information, see CREATE API INTEGRATION.
CREATE OR REPLACE API INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration API_PROVIDER = git_https_api API_ALLOWED_PREFIXES = ('https://example.com/my-account') ALLOWED_AUTHENTICATION_SECRETS = ALL USE_PRIVATELINK_ENDPOINT = TRUE ENABLED = TRUE;
Provide credentials in a basic authentication secret.
After successfully connecting to the Git server over private link, you must still authenticate with the repository by creating another secret that provides credentials for the repository.
To provide the credentials that Snowflake uses to authenticate with the repository, create a secret that contains the following:
A TYPE value of
passwordA username and token, such as a personal access token (PAT)
Note
For information about creating a personal access token in GitHub, see Managing your personal access tokens in the GitHub documentation.
For more information on the SQL command for creating a secret, see the CREATE SECRET.
Create a Git repository clone as described in Create a Snowflake Git repository clone.
Create a Snowflake Git repository clone¶
To set up Snowflake to work with a remote Git repository, create a Git repository clone in Snowflake to contain files fetched from the remote repository.
Note
Before beginning the steps in this section, consider first configuring components you might need, including a secret (if the remote repository requires authentication), an API integration, and private link connection between Snowflake and your cloud service provider.
Note
For information on creating a Git workspace in Snowsight, see Create a Git workspace.
A Git repository clone in Snowflake specifies the following details:
The remote repository’s origin
In Git,
originis the remote repository’s URL. Use that URL when setting up Snowflake to use a remote Git repository. The URL must use HTTPS. For example, you can retrieve the origin URL in the following ways:In the GitHub user interface, you can get the origin URL from the repository home page. Select the Code button, and then copy the HTTPS URL from the box displayed beneath the button.
From the command line, use the
git configcommand from within your local repository, as in the following example:$ git config --get remote.origin.url
The command produces output such as the following:
https://github.com/my-account/snowflake-extensions.gitFor reference information about
git config, see the git documentation.
Credentials, if needed, for Snowflake to use when authenticating with the repository
For the GIT_CREDENTIALS parameter, specify a Snowflake secret you created.
An API integration specifying details for Snowflake interaction with the repository API
You can create a Git repository clone by using either Snowsight or SQL.
Note
Before creating a Git repository clone, you’ll need to create a secret (if the remote repository requires authentication) and an API integration.
Code in the following example creates a Git repository clone called snowflake_extensions. The clone specifies
the my_git_api_integration API integration and the my_git_secret secret with credentials for authenticating.
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN;
GRANT CREATE GIT REPOSITORY ON SCHEMA myco_db.integrations TO ROLE myco_git_admin;
GRANT USAGE ON INTEGRATION my_git_api_integration TO ROLE myco_git_admin;
GRANT USAGE ON SECRET db.schema.my_git_secret TO ROLE myco_git_admin;
USE ROLE myco_git_admin;
CREATE OR REPLACE GIT REPOSITORY snowflake_extensions
API_INTEGRATION = my_git_api_integration
GIT_CREDENTIALS = my_git_secret
ORIGIN = 'https://github.com/my-account/snowflake-extensions.git';
Note
For information on creating a Git workspace in Snowsight, see Create a Git workspace.
Sign in to Snowsight.
In the navigation menu, select Catalog » Database Explorer.
In the object explorer, select the database and schema that you want to contain the Git repository clone you’re creating.
Select Create » Git Repository.
In the Create Git Repository dialog, for Repository Name, enter a name that will uniquely identify this repository clone in the schema.
For naming guidelines, see Identifier requirements.
For Origin, enter the remote repository’s origin URL.
From the API Integration drop-down menu, select the API integration to reference when creating the Git repository clone.
If you don’t have an API integration to use, select Create new API integration in Worksheets to use SQL to create one. For more information, see CREATE API INTEGRATION.
Optional: For the Comment, enter text describing this integration for others.
Optional: If the remote repository requires authentication, set the Authentication toggle to the _on_ position.
If you turned on the toggle, from the Secret menu, select the secret that should be referenced by the Git integration to authenticate with the remote repository.
If you don’t have a secret to use, select Create new secret in Worksheets to use SQL to create one. For more information, see CREATE SECRET.
Select Create.
When you successfully create the integration, the Git repository clone appears beneath the schema, in a Git Repositories directory. You’ll also see a page that lists repository directories, branches, and tags.
