Overview of the data lifecycle¶
Snowflake provides support for all standard SELECT, DDL, and DML operations across the lifecycle of data in the system, from organizing and storing data to querying and working with data, as well as removing data from the system.
Lifecycle diagram¶
All user data in Snowflake is logically represented as tables that you can query and modify through standard SQL interfaces. Each table belongs to a schema which in turn belongs to a database.
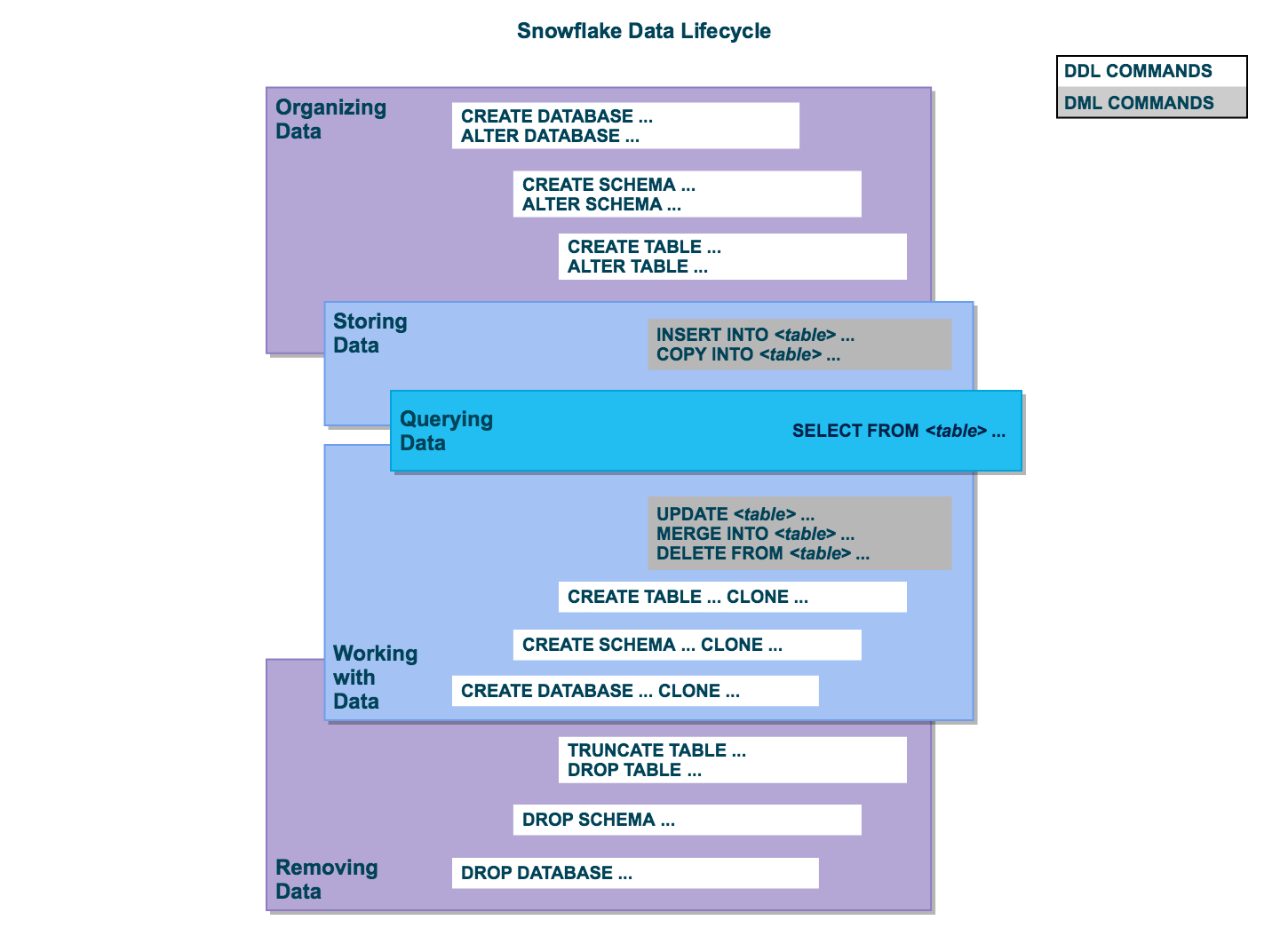
Organize data¶
You can organize your data into databases, schemas, and tables. Snowflake doesn’t limit the number of databases you can create or the number of schemas you can create within a database. Snowflake also doesn’t limit the number of tables you can create in a schema.
For more information, see the following topics:
Store data¶
You can insert data directly into tables. In addition, Snowflake provides DML for loading data into Snowflake tables from external, formatted files.
For more information, see the following topics:
Query data¶
After data is stored in a table, you can issue SELECT statements to query the data.
For more information, see SELECT.
Work with data¶
After data is stored in a table, you can perform all standard DML operations on the data. In addition, Snowflake supports DDL actions, such as cloning entire databases, schemas, and tables.
For more information, see the following topics:
Remove data¶
In addition to using the DML command, DELETE, to remove data from a table, you can truncate or drop an entire table. You can also drop entire schemas and databases.
For more information, see the following topics: