Cortex AI Functions: Documents¶
Snowflake provides advanced AI-powered document intelligence capabilities as Cortex AI Functions. These functions help you to process, parse, classify, and extract information from a wide variety of document types to power analytics, automation, and intelligent applications, all using simple SQL. Document functions help you with the following tasks:
Parse documents to convert unstructured text and layouts into structured, searchable, analyzable content.
Extract structured information (entities, tables, or fields) from documents.
Classify document types to drive downstream workflows and analytics.
Cortex document processing functions can be combined to build retrieval augmented generation (RAG) pipelines, intelligent search and chatbot systems, and large-scale document analytics. The following illustration shows how Cortex document processing functions form a composable framework in which components can be mixed and matched to build tailored solutions.
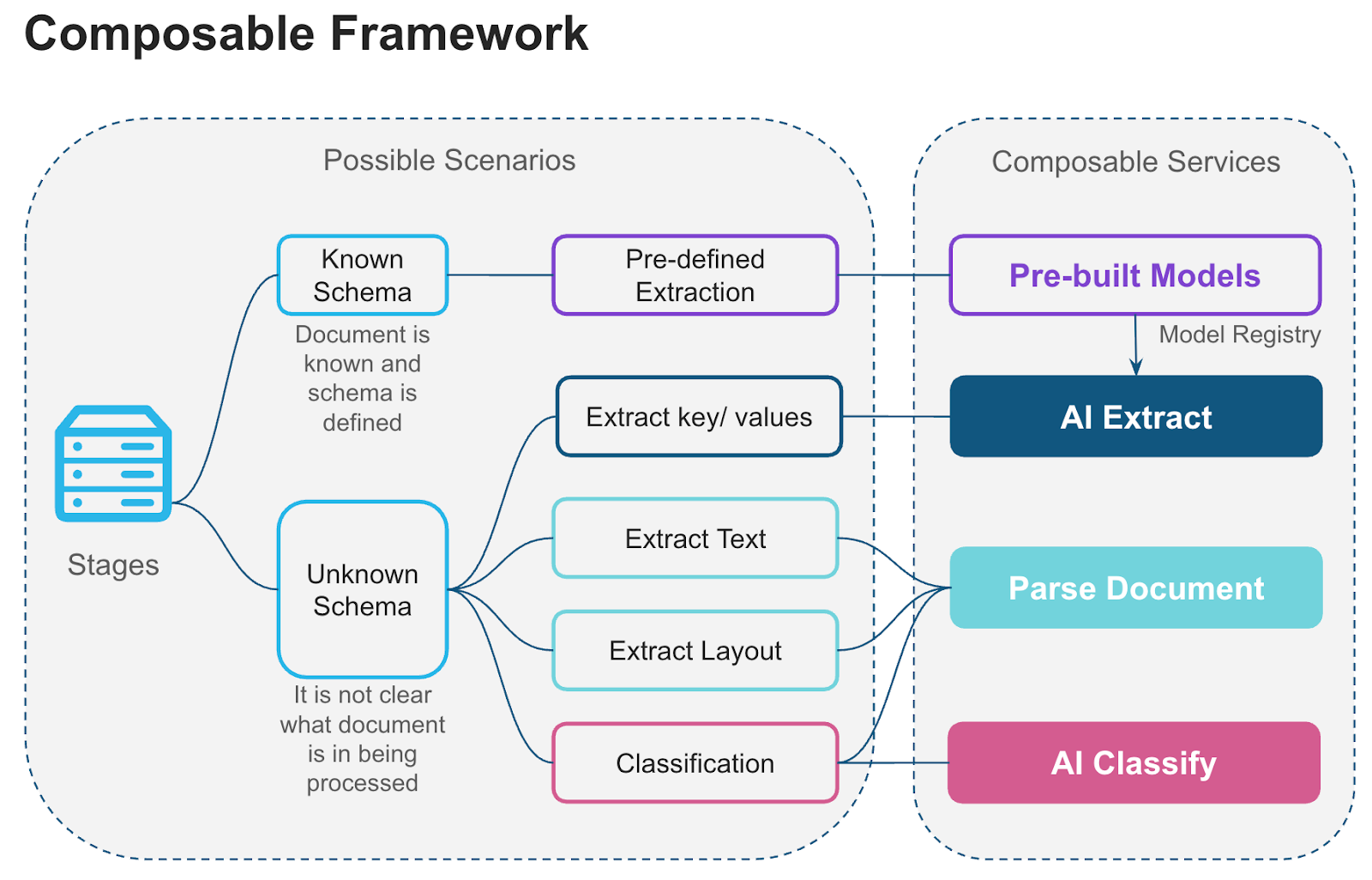
Document functions¶
The core Cortex AI Functions for document processing are:
AI_PARSE_DOCUMENT: Converts digital-native or scanned documents into rich text while preserving layout and context. Optionally extracts images from documents. Ideal for semantic search, RAG pipelines, and summarization workflows. Works well with document analysis that requires understanding the entire document content.
AI_EXTRACT: Provides high-quality structured extraction of information from documents. Understands text, tables, checkboxes, handwriting, and other visual elements. Specializes in extracting structured data based on a schema.
AI_COMPLETE: The most general-purpose AI Function, AI_COMPLETE generates text completions based on a prompt you provide, and so can be used for a wide variety of tasks involving extracting or transforming text from documents. An advantage of AI_COMPLETE is the ability to choose a model.
The following text-processing AI Functions can be used to further analyze or transform text extracted from documents.
AI_SENTIMENT: Analyzes the sentiment of text content.
AI_TRANSLATE: Translates text content between languages.
SUMMARIZE: Generates concise summaries of text content.
Use cases¶
Cortex AI Functions for document processing are designed to be used together or individually to address a variety of use cases, and are well-suited for these two use cases:
Building RAG pipelines for chatbots and enterprise search services¶
Documents processed by AI_PARSE_DOCUMENT can be indexed by Cortex Search Services, which can act as retrieval augmented generation (RAG) engines to improve language model responses to user queries. In this scenario, you use the Cortex Search Service to find documents related to the query, then pass these documents to AI_COMPLETE as part of the prompt to generate more contextually relevant responses.
Building document processing pipelines for streamlining workflows and analytics¶
Cortex document processing AI Functions help you build intelligent, flexible, and scalable document processing pipelines using modular components. Such a pipeline ingests documents in various formats and transforms them into actionable data, allowing you to build workflows like these:
Schema based extraction: Apply a natural language schema to extract entities – ranging from single entities to complex tabular data – from a set of documents
Q&A against document: Ask questions about a document in natural language.
Text and layout extraction: Capture document text (with or without layout) to extract entities, generate summaries, and perform analysis using other AI Functions.
Classification: Determine the document type (e.g., “invoice,” “contract,” “report”) when ingesting data to route each type to an appropriate processing workflow.
Build a model registry to share custom extraction and classification models: A model registry stores document extraction models fine-tuned for custom use cases specific to your organization. Reusing these models across teams saves time and effort.