Snowflake Postgres instance management¶
Snowflake Postgres helps you manage your instances through a variety of instance management operations. These operations are forms of maintenance that keep your instances operational and secure.
A brief service interruption is required to perform instance management operations. Please ensure that your applications are able to automatically reconnect to the database.
Note
An instance’s connection string will remain the same across instance management operations unless you explicitly rotate the credentials.
When required to ensure the health of your instance, we may schedule maintenance operations on your behalf (for example, to modify instance storage size).
For a detailed description of how instance maintenance is carried out by our platform, see Snowflake Postgres Maintenance.
Available operations¶
The following operations are available from the Manage dropdown menu on your instance details page in the dashboard:
Fork - Create a new instance from an existing instance
Modify - Change the instance size, storage size, or Postgres version of the instance
Enable High Availability - Enable High Availability for the instance
Create replica - Create a replica of the instance
Instance Suspend and Resume - Spin down the Postgres server but retain data on disk
Restarting services - Restart either PostgreSQL or the entire underlying server
Regenerate credentials - Regenerate the credentials for the instance
Fork¶
You can fork an instance to create a new instance from an existing instance, optionally choosing a point in time to fork from. By default the new instance will be forked from the current state of the source instance. Read more about forking in Snowflake Postgres point-in-time recovery.
Modify¶
To make a change to an existing Snowflake Postgres instance, you must use a role that has been granted the OWNERSHIP or OPERATE privilege on that instance.
You can resize an instance in-place with minimal impact and no changes to your connection string. During an instance resize, you can:
Change the COMPUTE_FAMILY to a different size.
Change the amount of storage. Both increases and decreases in storage size are supported.
Upgrade the Postgres version to a newer major version.
Modifying your instance’s configuration requires maintenance. See Snowflake Postgres Maintenance for more information.
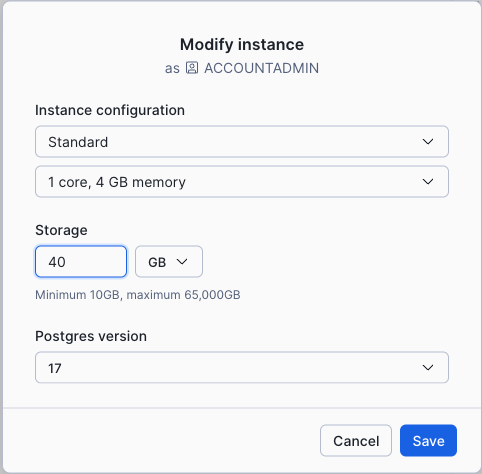
To make a change:
In the navigation menu, select Postgres.
Select your instance.
In the Manage menu at the top right, select Modify.
Select the new COMPUTE_FAMILY and/or storage size from the dropdown menus. See Postgres major version upgrades for more information about changing the Postgres version.
Select the Save button to confirm the changes.
Run the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE command to make changes to the configuration of a Snowflake Postgres instance.
Note
The changes to the instance are applied as an asynchronous operation.
To check the status of the operation, run the DESCRIBE POSTGRES INSTANCE command.
NETWORK_POLICY = policy_nameSpecifies the network policy to use for the instance. Changes to the policy may take up to 2 minutes to take effect.
To specify this parameter, you must have been granted the USAGE privilege on the NETWORK_POLICY object.
HIGH_AVAILABILITY = { TRUE | FALSE }Enables Snowflake Postgres High Availability for the instance. Executes as an asynchronous operation. DESCRIBE may be used to track its progress in the operations field. An HA change may only be initiated if the instance is in the READY state and may not be initiated if any other operation is running (including an HA enablement/disablement)
Default:
FALSECOMPUTE_FAMILY = compute_family.STORAGE_SIZE_GB = storage_gb.POSTGRES_VERSION = 16 | 17
These operations are collectively referred to as “upgrade” operations and are performed together.
DESCRIBE POSTGRES INSTANCEmay be used to track its progress in the operations fieldAn upgrade operation may only be initiated if the instance is in the READY state and may not be initiated if any other operation is running
If an instance has a defined maintenance window, the changes will not take effect until the maintenance window period, unless
APPLY IMMEDIATELYhas been specified to override the maintenance window.POSTGRES_SETTINGS = 'json_string'Specifies the changes to the Postgres settings for the instance. Specify the settings in a JSON-formatted string with the following structure:
Changes to some of the Postgres settings may require an instance restart to take effect. These changes will not take effect unless you specify
APPLY IMMEDIATELYin the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE statement. For the list of settings that require a restart, consult the table in Postgres settings.MAINTENANCE_WINDOW_START = hour_or_dayThe desired hour of day which a maintenance window can possibly start. This should be an integer from 0 to 23 representing the hour of day which maintenance is allowed to start, with 0 representing midnight UTC. Maintenance windows are three hours starting from the specified hour. Unsetting an existing maintenance window causes all ongoing operations to be applied as soon as they have completed.
APPLY IMMEDIATELYIf the cluster has a defined maintenance window,
APPLY IMMEDIATELYoverrides the maintenance window for all specified operations to be applied as soon as they are ready.APPLY IMMEDIATELYapplies only toCOMPUTE_FAMILY,STORAGE_SIZE_GB,POSTGRES_VERSION, andPOSTGRES_SETTINGS. For all other options it is ignored.APPLY ON 'timestamp'If the cluster has a defined maintenance window,
APPLY ONoverrides the maintenance window for all specified operations to be applied at the timestamp provided.APPLY IMMEDIATELYmay not be specified withPOSTGRES_SETTINGS. The specified timestamp may not be more than 72 hours in the future and may be of the following forms:
yyyy-MM-dd
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm zzz
Modifying a Postgres instance examples
Change an existing instance’s COMPUTE_FAMILY to STANDARD_M and storage size to 100GB in a single operation:
If you plan to decrease the storage size of your instance, please note that we currently allow the resize to be greater than or equal to 1.4x the current disk usage to reduce alerting and immediate resizing up.
Postgres major version upgrades¶
Snowflake Postgres allows you to schedule your major version upgrades through the Dashboard. To make this change, you’ll use the same process as for an instance resize.
Tip
Upgrading your instance to a new major version requires maintenance. See Snowflake Postgres Maintenance for general information about maintenance.
To initiate a major version upgrade, you must use a role that has been granted the OWNERSHIP or OPERATE privilege on the instance.
Note
You can only upgrade to a newer major version. You can’t downgrade to a previous major version.
You can combine a major version upgrade with an instance resize by selecting a new instance size, storage size, or both along with the new version number.
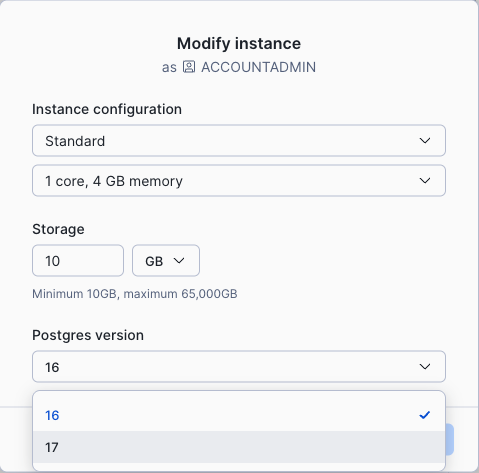
In the navigation menu, select Postgres.
Select your Snowflake Postgres instance.
In the Manage menu at the top right, select Modify.
If a newer version is available, you will be able to select it from the Postgres version dropdown menu.
Select the Save button to confirm the change.
You can initiate a major version upgrade with the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE command, by setting the POSTGRES_VERSION parameter to the desired version.
POSTGRES_VERSION = { 16 | 17 }The desired Postgres version to upgrade to.
Example: Upgrade an existing instance to PostgreSQL 17
Example: Combine a major version upgrade with an increase in storage size
Postgres major version upgrades work differently than other instance management operations. Once you initiate the process, Snowflake Postgres will execute the following steps:
Create a “hidden” (not visible to users) replica of your current instance.
Migrate existing data from the source instance to the hidden replica (duration is relative to data size).
When your maintenance window arrives:
Lock the source instance to prevent writes.
Upgrade the hidden replica (duration depends on the number of objects in your database, not data size).
Fail over to the newly upgraded instance once the upgrade is complete.
Important Notes:
Major Version changes can affect application compatibility. We recommend testing your application against the new PostgreSQL version before upgrading.
Read Replicas are automatically upgraded when performing a major version upgrade, but only once its primary is upgraded and a fresh backup is taken. Until then, replicas will remain available but in a stale state.
If you have no maintenance window set, and have not specified a run time, the upgrade will commence as soon as the new instance is populated and ready.
This operation creates a service interruption that should last no longer than a few minutes.
If an upgrade fails, your instance will automatically revert back to the original instance.
Enable High Availability¶
When High Availability (HA) is enabled, your instance includes a standby host that replaces the primary if your primary becomes unavailable. You can read more about this in Snowflake Postgres High Availability.
Create replica¶
You can create a replica of your instance from the dashboard. A replica is a read-only copy of the source instance that is kept in sync with the source instance. Find about more about creating and using replicas in Snowflake Postgres Read Replicas.
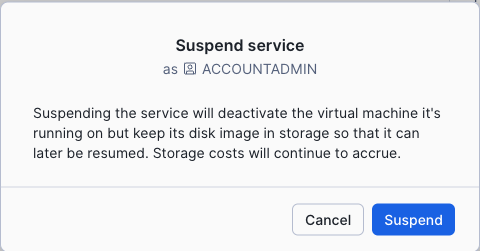
Instance suspend and resume¶
Suspending an instance deactivates the virtual machine that it’s running on while keeping its disk image in storage so that the instance can be resumed. Normal billing for the instance is suspended, but storage costs will continue to accrue. The existing 10 days’ worth of backups are also retained.
If there were operations that were pending restart to be applied, they will be applied when the instance is resumed.
To suspend or resume a Snowflake Postgres instance, you must use a role that has been granted the OWNERSHIP or OPERATE privilege on the instance.
To suspend a Snowflake Postgres instance, run the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE command with the SUSPEND option. For example:
These operations are asynchronous. You can use the DESCRIBE POSTGRES INSTANCE command to track the status of these operations.
Example: Suspend a Snowflake Postgres instance named my_instance
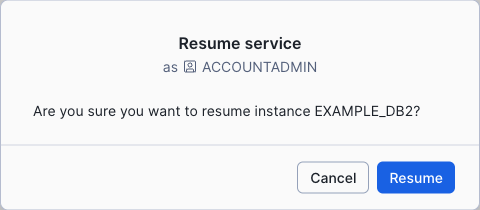
You can resume a suspended instance at any time. The time it takes to resume an instance depends on the instance and the size of the dataset. When you resume an instance, normal billing and backups will also recommence.
To resume a Snowflake Postgres instance, run ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE … RESUME:
These operations are asynchronous. The DESCRIBE command may be used to track the status of these operations.
Example: Resume a Snowflake Postgres instance named my_instance
Restarting services¶
You can restart either PostgreSQL or the underlying server that runs your Postgres instance if needed. This type of instance management operation restarts the server in-place, without creating a replica or performing a fail-over. Read more about restarting services in Snowflake Postgres Maintenance.
Regenerate credentials¶
Regenerating credentials will return a new connection string for your database instance, replacing the existing credentials. Read more about this topic in Snowflake Postgres Roles.
Custom configuration parameters¶
You can make changes to many of Postgres’s own server settings for your Snowflake Postgres instances. You can see the list of available configuration parameters in Snowflake Postgres Server Settings.
To change the Postgres settings on a Snowflake Postgres instance, you must use a role that has been granted the OWNERSHIP or OPERATE privilege on that instance.
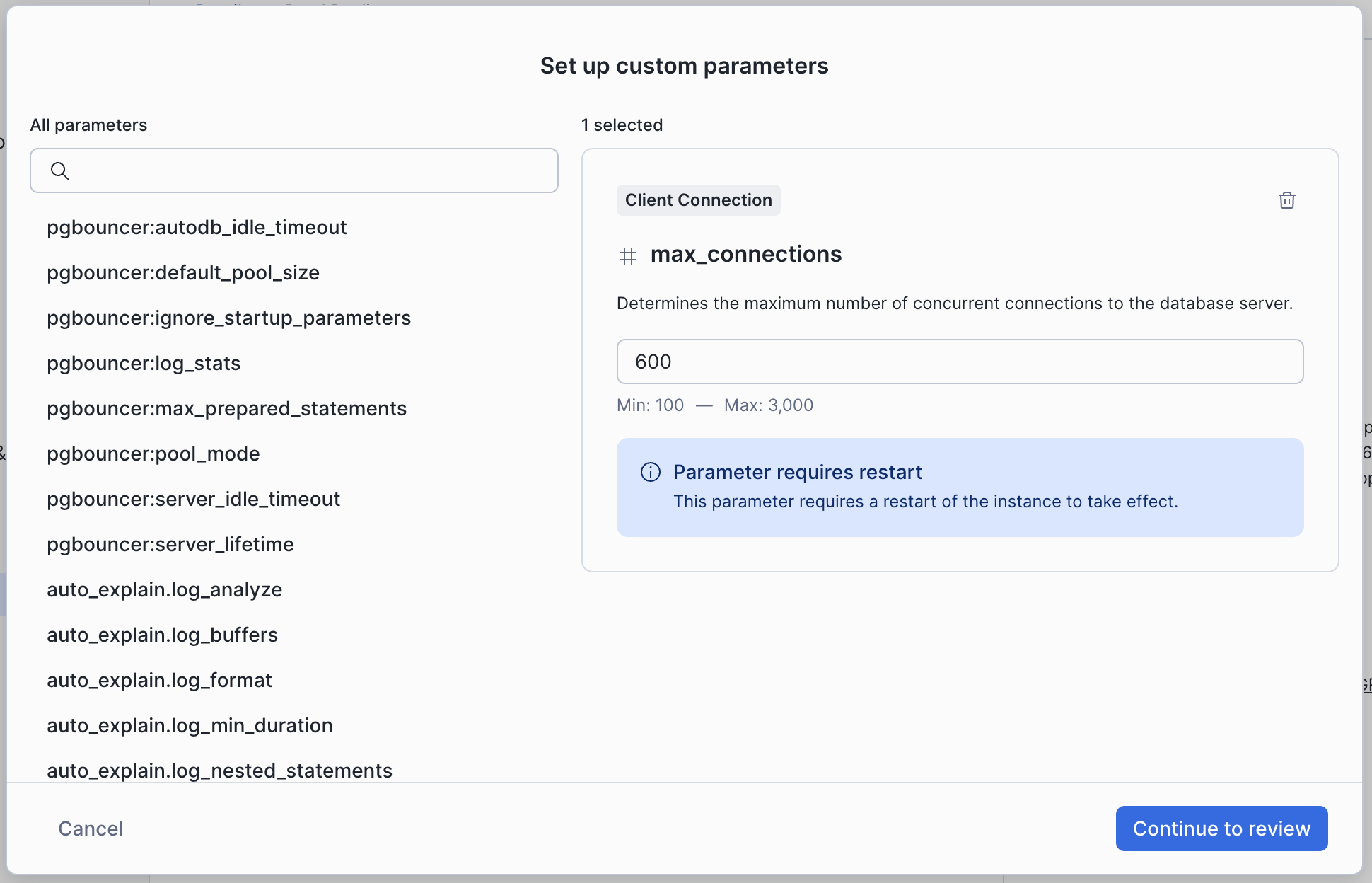
To make a change:
In the navigation menu, select Postgres
Select your instance
On the right side of the page select the edit icon next to Custom parameters
Choose configuration parameters from the list, or use the search box to find specific parameters.
Enter the new value for the configuration parameter.
When you’ve finished add new values for parameters, click Continue to review, and then click Submit to confirm the changes.
To specify changes to the Postgres settings for the instance, run the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE command with the SET POSTGRES_SETTINGS option.
With the POSTGRES_SETTINGS option, you specify a JSON-formatted string with the following structure:
Changes to some of the Postgres settings may require an instance restart to take effect. These changes will not take effect unless you specify APPLY IMMEDIATELY in the ALTER POSTGRES INSTANCE statement. For the list of settings that require a restart, consult the table in Postgres settings.
Example: Set the work_mem configuration parameter to 128MB for a Snowflake Postgres instance named my_instance
Instance states¶
Any instance management operation, whether it’s creating a new instance or modifying an existing
one, takes some time to complete. The exact duration depends on many factors, including your
data and schema sizes, and how busy your instance is. An instance’s state gives
you insight into the progress of an ongoing operation. It is shown in the dashboard, or you can
check it by running the DESCRIBE POSTGRES INSTANCE command.
Possible instance states are listed below. During an instance modification operation, the replacement instance goes through all of the states listed in the first table. A new instance being created goes through some but not all of the states listed. The following table lists some additional states you might see during normal operations.
States seen during create, modify, and fork:
State |
What’s happening |
Typical duration |
Next state |
|---|---|---|---|
Creating |
A new underlying server is being created |
1-2 minutes |
Restoring |
Restoring |
Latest base backup is being restored to the server |
Variable |
Starting |
Starting |
Postgres is being started on the instance and WAL that accumulated during base backup is being applied |
Variable |
Replaying |
Replaying |
Accumulated WAL since last base backup is being replayed |
Variable |
Finalizing |
Finalizing |
Instance configuration is being finalized and the server is being made available |
1-2 minutes |
Ready |
Ready |
New instance matches source instance and is ready for the operation to proceed. If scheduled
for an upcoming maintenance window, the instance is kept |
N/A |
N/A |
Other instance states that you might see on the platform:
State |
What’s happening |
Typical duration |
Next state |
|---|---|---|---|
Restarting |
Underlying server is being restarted |
1-2 minutes |
Ready |
Resuming |
A new server is being built and a suspended instance is being resumed |
3-5 minutes |
Ready |
Suspending |
Instance is being suspended |
3-5 minutes |
Suspended |
Suspended |
Instance is currently suspended |
Until resumed |
Resuming |