Application roles: Allow consumers to share different views of the same data¶
As a provider, you can enhance the consumer experience by including application roles in your Declarative Native App. An application role is a credential created within the context of a Declarative Native App. For information about application roles, see About application roles.
Application roles isolate security for the application, so that the application’s specific security credentials don’t need to be managed within the consumer’s broader organizational security model. Using application roles, providers can control access to application resources simply. Consumer accounts can then grant access to application logic and data using simple SQL GRANT statements.
For example, if an application uses an Operations application role to access a log table, the consumer doesn’t need to maintain that application role outside the context of the application; they only need to know that they can share the application with their support team using the Operations application role.
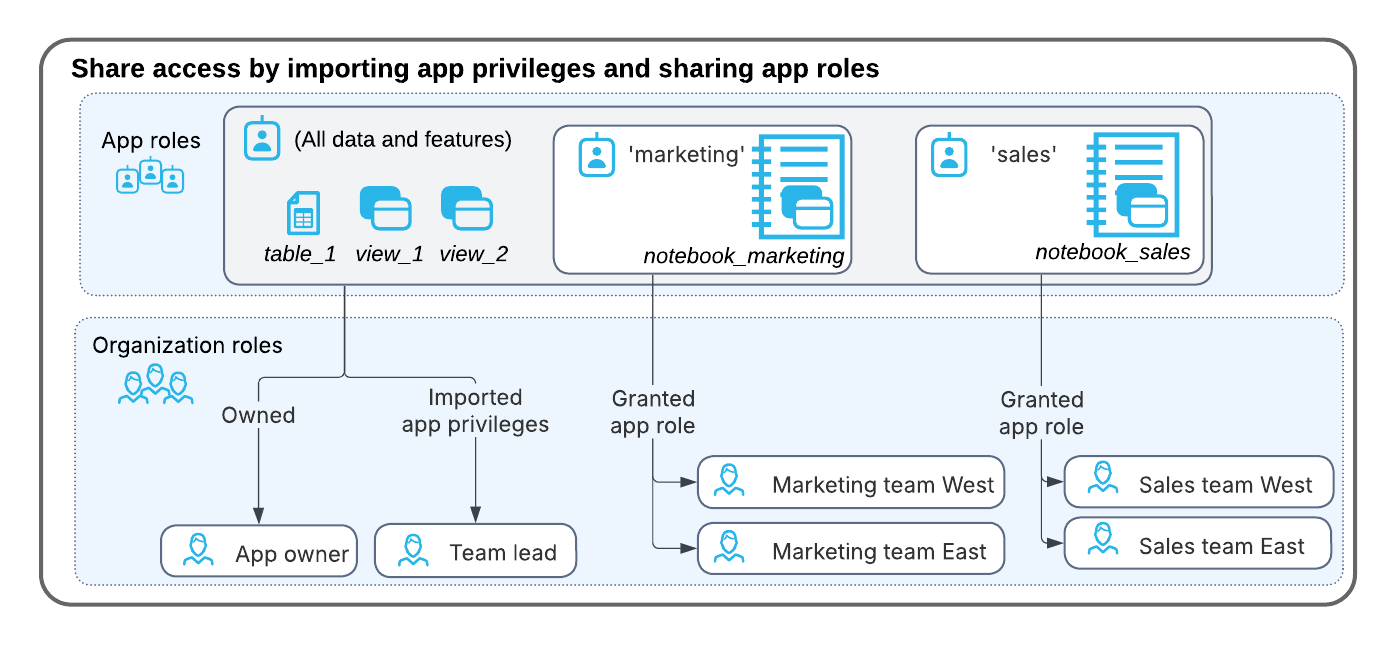
Using the manifest file, you define application roles, and assign them to content in the app. When the consumer installs the app, they can share the content with their organization members by assigning the application roles to their account roles and users. Consumers can also create hierarchies of application roles by assigning application roles to other application roles.
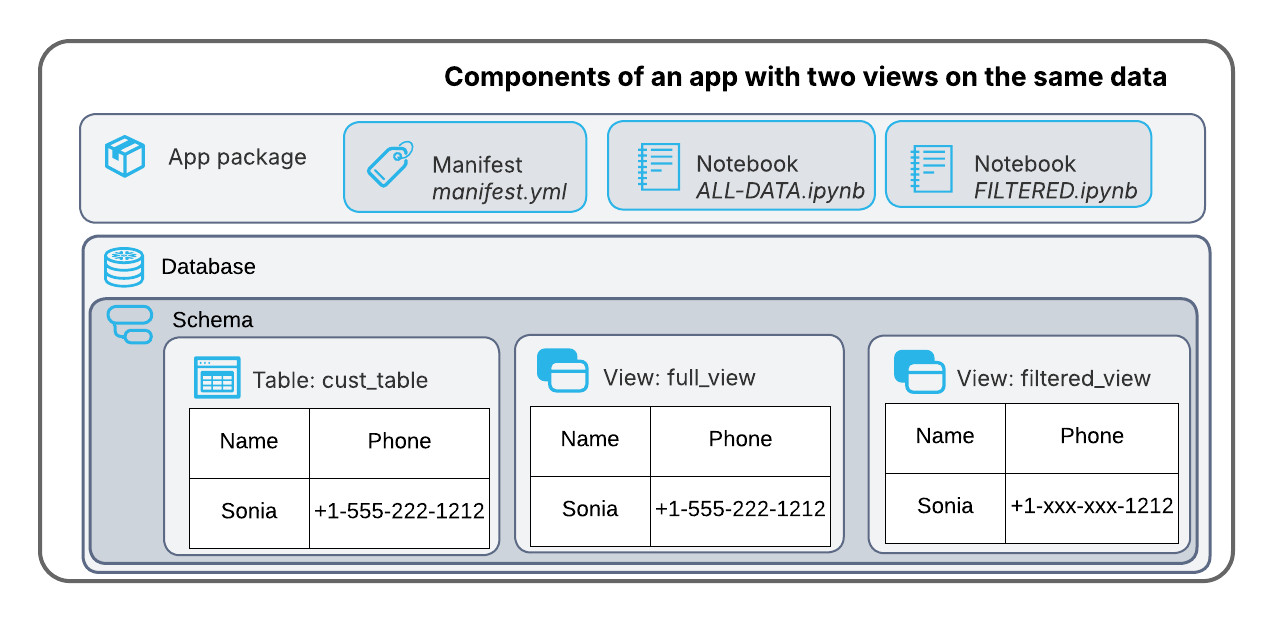
Application roles allow consumers to share data in different ways with members of their organization. For example, an app can include two notebooks to present the data, with one that includes a full view of the data, and the other a filtered view.
The consumer app owner can then choose to share a filtered view with a team, while still having access to the full view for themselves.
When you use application roles to permit access to database resources, the child resources inherit the roles of their parent resources. For example, if you assign an application role to a schema, all tables and views in that schema inherit the role. If you assign an application role to a database, all schemas, tables, and views in that database inherit the role.
Assign application roles to content in the manifest file¶
In the manifest file, in the top-level roles field, define the available application roles, for example,
sales,marketing, andoperations.roles: - sales: comment: "The sales role provides access to the filtered view of the sales data." - marketing: comment: "The marketing role provides access to the filtered view of the marketing data." - operations: comment: "The operations role provides access to the full view of the data, including logs."
CopyAssign app roles to the contents of the manifest file, using a list. for example,
roles: [sales, support]:- customer_table: roles: [sales,marketing] # Accessible to sales and marketing, app owners
CopyTo add a table, add the role to both
<named table>.rolesand to<named schema>.roleswhere the table resides.schemas: - sales_table: roles: [sales] tables: - sales_table: roles: [sales]
CopyTo add a view, add the role to both
<named view>.rolesand to<named schema>.roleswhere the view resides.schemas: - sales_view: roles: [sales] views: - sales_view: roles: [sales]
CopyWhen adding a filtered view of a table, don’t add the underlying table; this prevents users from accessing the unfiltered data.
To include a notebook, add the role to
<named notebook>.roles, and add the tables and views (and their underlying schemas) referenced in the notebook.notebooks: - SALES_NB: main_file: ALL-DATA.ipynb roles: [sales] comment: Accessible to sales and app owners, references full view of the sales data
CopyWhen adding a notebook that references a filtered view of a table, don’t add the underlying table; this prevents users accessing the unfiltered data.
To give an object no app roles, either leave the field empty (
[]) or omit it. These objects are only accessible by the app owner and roles with granted IMPORTED PRIVILEGES.
- my_schema: roles: [] # Accessible to app owners onlyCopy
Example manifest file:
roles:
- sales:
comment: "The sales role provides access to the filtered view of the sales data."
- marketing:
comment: "The marketing role provides access to the filtered view of the marketing data."
- operations:
comment: "The operations role provides access to the full view of the log data."
application_content:
notebooks:
- SALES_NB:
main_file: ALL-DATA.ipynb
roles: [sales]
comment: Accessible to sales and app owners, references full view of the sales data
- MARKETING_NB:
main_file: FILTERED.ipynb
roles: [marketing] #
comment: Accessible to marketing and app owners, references filtered view of the marketing data
shared_content:
databases:
- my_database:
schemas:
- my_schema:
roles: [] # Accessible to app owners
tables:
- sales_table:
roles: [sales] # Accessible to sales, app owners
- marketing_table:
roles: [marketing] # Accessible to marketing, app owners
- customer_table:
roles: [sales,marketing] # Accessible to sales and marketing, app owners
- logs_table:
roles: [operations] # Accessible to operations and app owners
views:
- sales_view:
roles: [sales] # Accessible to sales and app owners
- marketing_view:
roles: [marketing] # Accessible to marketing and app owners
- customer_view:
roles: [sales,marketing] # Accessible to sales, marketing, and app owners
- operations_view:
roles: [operations] # Accessible to operations and app owners
Later, when the consumer installs the app, they’ll have access to both notebooks, the tables, and the views.
To share the operations view with their support team, they grant the operations application role to their support team organization role.
GRANT APPLICATION ROLE customer_app.operations TO ROLE support_team_west;
Consumer team members with the support_team_west role can see the logs table, but they can’t see the notebooks in the Available Notebooks tab in Snowsight, or access the sales and customers tables and views.
To share the sales view with their sales team, they grant the sales application role to their sales organization role.
GRANT APPLICATION ROLE customer_app.sales TO ROLE sales_team_east;
Consumer team members with the sales_team_east role can see the notebook in the Available Notebooks tab in Snowsight. They can’t see the logs table, but can access the sales and customers tables and views.
For more information about how consumers share roles, see Share access to the app.