Cortex Code in Snowsight¶
Overview¶
Cortex Code provides an agentic experience across several functional areas within Snowsight. It is designed to assist data analysts, engineers, and administrators with tasks such as SQL development, data exploration, and account management by deeply integrating into the Snowsight interface and offering capabilities such as diff views.
Cortex Code uses intelligent orchestration to plan and execute multi-step tasks based on your request. In addition, it selects internal tools and relevant context from your Snowflake environment to complete the task, ensuring that each response is accurate.
The assistant follows an agentic workflow and interprets your intent, creates a plan of action, and executes the steps while maintaining context across the session.
Cortex Code understands roles, privileges, schemas, and SQL syntax, and applies Snowflake best practices when it is generating or modifying code.
To use Cortex Code in Snowsight, follow these steps:
Select the Cortex Code icon
 in the lower-right corner. The Cortex Code panel opens on the right side of Snowsight.
in the lower-right corner. The Cortex Code panel opens on the right side of Snowsight.In the message box, type in your question and then select the send icon or press Enter to submit it. Cortex Code provides a response in the panel.
If the response from Cortex Code includes SQL statements, you can execute the statements or copy them to your clipboard.
Access control requirements¶
A role used to access Cortex Code must have the following database roles granted:
Database Role |
Notes |
|---|---|
SNOWFLAKE.COPILOT_USER |
Required for all users to access Cortex Code. |
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_USER or SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_AGENT_USER |
At least one of these database roles is required. SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_AGENT_USER provides additional capabilities for agentic workflows. |
For instructions on granting database roles, see GRANT DATABASE ROLE.
For general information about roles and access control, see Overview of Access Control.
Note
If your account previously opted out of (or disabled) Snowflake Copilot (legacy), Cortex Code will also be disabled. Contact your account team to enable this feature for your account.
Use cases and benefits¶
Cortex Code in Snowsight acts as an intelligent agent, helping you work more efficiently by translating natural language instructions into executable actions. By maintaining awareness of your workspace context and Snowflake account configuration, it assists with development, exploration, and administration tasks without requiring you to leave Snowsight.
Cortex Code supports the following key functional areas within Snowsight:
Agentic coding in Workspaces¶
Cortex Code operates as a conversational coding assistant integrated within Workspaces. It supports interactive code generation, modification, review, and explanation.
Code generation and development: Generate SQL queries, create new files, and construct logic for data pipelines and analytics workflows.
Code modification and optimization: Refine SQL directly in a workspace, identify logic or syntax errors, and suggest optimizations for performance, readability, or cost.
Change review: Preview AI-suggested changes using a diff view before applying them. The diff view highlights insertions and deletions, allowing users to maintain control over their code.
Code explanation: Request an explanation of existing SQL to assist with understanding or collaboration.
Ask follow-up questions: Continue the conversation by asking clarifying questions or requesting further analysis on generated code or results.
Quick actions from highlighted SQL: In a SQL file, highlight text to open quick actions such as Quick Edit, Format, Add to Chat, and Explain.
Fix SQL errors: If a SQL statement fails, use the Fix button in the results grid to get suggested fixes for the error.
Intelligent product and documentation discovery¶
Cortex Code uses context from the Horizon Catalog and Snowflake documentation to help you locate data assets and reference information without leaving your workspace.
Natural language schema search: Locate database objects such as tables and columns using plain language queries, without needing to know exact object names.
Integrated Q & A: Retrieve answers about Snowflake features, SQL syntax, or best practices based on official documentation.
Snowflake Marketplace discovery: If your prompt references Snowflake Marketplace, Cortex Code will search and return listings from the Snowflake Marketplace.
When available, responses can include relevant context such as tags, masking policies, and lineage to help you validate the data assets you discover.
Simplified account administration¶
Cortex Code supports account administration by providing contextual information about governance, security, and cost management.
Governance and security: Retrieve information about user and role access, data ownership, and tables containing personally identifiable information (PII).
Cost management: Query account usage and credit consumption, and identify high-cost warehouses or queries.
Supported models and regions¶
Cortex Code supports the following models. You can use these models as long as the account has access to them. For more information, see Control model access.
Recommended: Claude Opus 4.5 (
claude-opus-4-5)Claude Sonnet 4.5 (
claude-sonnet-4-5)Claude Sonnet 4.0 (
claude-4-sonnet)
While the listed models may not be available in all regions, you can use Cortex Code in any cloud or region by using Cortex Cross-region inference. This includes clouds and regions where the models are not available. For more information, see Cross-region inference.
Important
Cross-region inference is required when the selected model is not available in your region. If inference fails with a model availability error, configure cross-region inference:
AWS US - Claude Sonnet 4+ offers the highest quality. Set up Cortex Cross-region inference for
AWS_USto access Claude Sonnet 4.x models.AWS EU - Set up Cortex Cross-region inference for
AWS_EUto access Claude models.AWS APJ - Set up Cortex Cross-region inference for
AWS_APJto access Claude models.Any region - Set up Cortex Cross-region inference for
ANY_REGIONto access all models.
To enable cross-region inference, an ACCOUNTADMIN must run:
ALTER ACCOUNT SET CORTEX_ENABLED_CROSS_REGION = 'AWS_US';
Replace AWS_US with the appropriate region identifier (AWS_US, AWS_EU, AWS_APJ, ANY_REGION).
Note
Model access may also be restricted by your organization. If you cannot access a model even after enabling cross-region inference, verify that the model is enabled in your account’s AI model access settings. See Control model access for details.
Cortex Code requires the user to have the SNOWFLAKE.COPILOT_USER database role and either the SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_USER or SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_AGENT_USER database role.
Note
If your account previously opted out of (or disabled) Snowflake Copilot (legacy), Cortex Code will also be disabled. Contact your account team to enable this feature for your account.
Web search¶
An ACCOUNTADMIN role can configure Cortex Code CLI to search the web, and use the results in generating responses and planning tasks. To properly enable web search in an account, follow these steps:
Navigate to AI/ML > Agents.
Select Settings.
Select the toggle next to Web search to enable the feature, as shown below.
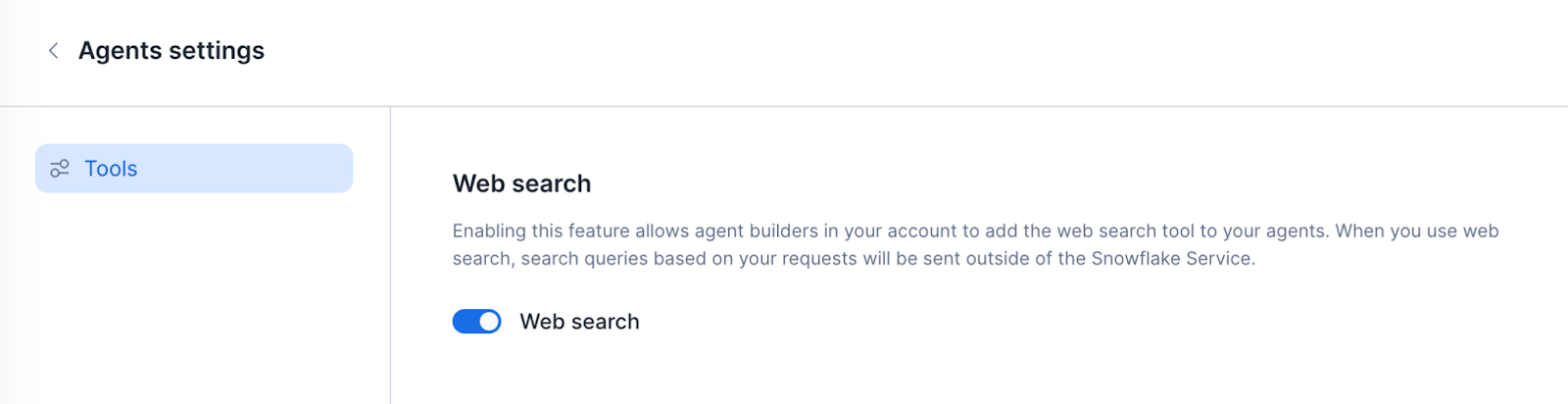
Snowflake will process your inputs according to the Snowflake Privacy Notice (§2). Web search may not be used for the purpose of redistributing or creating a competing web search service.
Example prompts¶
You can interact with Cortex Code using natural language prompts. In your prompts, provide the context needed to generate accurate results (for example, the database, schema, and the objects you want to work with). For the most reliable results across environments, use fully qualified object names.
The following examples show typical ways to request code generation, optimization, and administrative insights.
Access and permissions
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Access discovery |
“What databases do I have access to?” |
Security auditing |
“Find all tables that have PII in them.” |
Data discovery
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Tag discovery |
“List every table tagged PII = TRUE in ANALYTICS_DB.” |
Lineage and tagging |
“Show the lineage from RAW_DB.ORDERS to downstream dashboards.” |
Metadata search |
“Where can I find tables related to customer churn and subscription status?” |
SQL development and optimization
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Logic explanation |
“What does this SQL script do?” |
Generation |
“Write a query for top 10 customers by revenue and a 7-day moving average.” |
Query refinement |
“Update the top performers query to show the top 100.” |
Performance optimization |
“Explain why this query is slow and optimize it.” |
Data synthesis |
“Generate synthetic data for 30 days of sales for an e-commerce site in the SAMPLESDATA.SALES table.” |
Infrastructure and cost management
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Resource monitoring |
“Which 5 service types are using the most credits? Show me a visualization and how to reduce costs.” |
Machine learning and engineering pipelines
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Notebooks (EDA and machine learning) |
“Build me a notebook for a customer churn prediction use case using pandas for data handling, matplotlib and seaborn for EDA and visualization, and scikit-learn for preprocessing, model training (logistic regression and a tree-based model), evaluation, and interpretation, with clear markdown explaining business impact and results.” |
Deep learning |
“Create a new notebook and build a CNN for the MNIST dataset.” |
Pipeline engineering |
“Create a dbt project to transform raw sales data.” |
Semantic model integration (Cortex Analyst)
Use case |
Example prompt |
|---|---|
Semantic queries |
“Use the @models/revenue.yaml semantic model to answer "What was revenue last month?"” |
Model debugging |
“Identify errors in my semantic model at @models/revenue.yaml” |
Security and access¶
Cortex Code operates within your Snowflake account’s existing authentication and role-based access controls (RBAC). It does not store or modify your credentials and only performs actions permitted by your current role.
Cortex Code in Workspaces¶
You can access Cortex Code through the assistant panel integrated into Snowsight. Cortex Code processes requests in the context of the active code or environment, or general Snowflake knowledge.
To use the Cortex Code agent in Workspaces:
Sign in to Snowsight.
In the navigation menu, select Projects » Workspaces.
Open a workspace containing the relevant file (for example, an existing SQL file).
Select the Cortex Code icon at the bottom-right of the workspace.
Enter a prompt or ask a question using natural language. See Example prompts for ideas.
Review the output. Cortex Code provides an answer, suggested code, or a modified query.
For coding tasks, Cortex Code may display a comparison view highlighting insertions and deletions. Review the suggested changes and apply them directly to the script.
Use subsequent prompts to refine the code, convert the file to a different object type (like a notebook or semantic view), or integrate advanced functions like AI SQL.
Customize Cortex Code in Workspaces with AGENTS.md and Agent Skills¶
AGENTS.md is a simple, open format for guiding coding agents.
Create an AGENTS.md file to provide persistent instructions that Cortex Code will automatically include in every conversation. Copy it to the root directory of your workspace for personalized instructions that apply to conversations with Cortex Code about your project.
Support for Agent Skills will be available soon.
Cortex Code in Notebooks¶
Leveraging Cortex Code helps you explore data, write and edit queries and code, visualize insights, and explain results seamlessly in Notebooks in Workspaces, accelerating end-to-end data science and machine learning development.
Cortex Code in Notebooks can:
Create and manage notebooks in the Workspaces directory
Add, remove, and reorder SQL, Python, and Markdown cells
Edit code using up-to-date pre-installed packages and proper notebooks syntax (for example, cell referencing)
Generate code for visualizing data using matplotlib, seaborn, plotly, and altair
Run an entire notebook or specific cells
Try out these example prompts.
Cortex Code agent for dbt Projects on Snowflake¶
Cortex Code supports transformation workflows that span the full dbt lifecycle:
Explore raw source data and infer relationships
Scaffold staging and intermediate models
Build multi-model DAGs and metrics
Add data quality tests and incremental logic
Run dbt commands
Generate and maintain project documentation
Using natural language prompts, the Cortex Code agent helps you explore data, author dbt models, add tests, optimize performance, and generate documentation through iterative feedback.
It reduces day-to-day data engineering work by automating boilerplate SQL, dependency management, testing, and documentation, while preserving control over project structure and logic.
Example prompts for dbt Projects¶
The Cortex Code agent supports both new and experienced dbt users. New users can explore newly onboarded Bronze-layer data, infer schemas, and scaffold staging models to establish a clean foundation. Experienced users can build complex data marts with incremental fact models, robust testing, and auto-generated documentation, while iterating quickly through validation cycles.
The following scenarios illustrate common ways to use Cortex Code with dbt Projects.
Use case |
Context |
Example prompt |
|---|---|---|
Explore sources |
Understand raw data schemas and relationships before modeling. |
“List all source tables in the bronze layer and summarize key columns, data types, and likely primary keys. Propose staging models for each source.” |
Prototyping |
Creating multi-model logic and DAGs. |
“Create models to compute daily profitability by truck and location. Generate the DAG and propose dependencies.” |
Data Quality |
Adding tests to |
“Add not_null and accepted_values tests to key dimensions. Suggest uniqueness tests for IDs based on inferred keys.” |
Incremental Logic |
Optimizing model performance. |
“Convert the main fact model to an incremental model partitioned by order_date, with merge behavior for late-arriving data.” |
Documentation |
Reducing maintenance overhead. |
“Generate docs for the project and draft descriptions for new models and key columns based on source context.” |
Cortex Code, Snowflake Intelligence, and legacy Copilot¶
While Cortex Code supports a broad range of coding and administrative tasks, it is distinct from standalone coding agents and other specialized AI systems within Snowflake.
The following table summarizes key differences between Cortex Code, Snowflake Intelligence, and the legacy Copilot experience.
Feature |
Cortex Code |
Snowflake Intelligence |
Snowflake Copilot (legacy) |
|---|---|---|---|
Use case |
Supports development and operational workflows in Snowflake, including authoring SQL, exploring data assets, and performing administrative tasks. |
Provides a natural language interface for asking complex questions about data and receiving analysis-focused responses. |
Previous iteration of Cortex Code for documentation help and basic SQL assistance. |
Primary integration |
Integrated directly into Snowsight and Workspaces. Provides context-aware assistance within the active workspace. |
Accessed through the Snowflake Intelligence UI and Cortex Agents API, enabling natural language interaction for insights and recommendations. |
Separate copilot for SQL and UI assistance. |
Scope of tasks |
Supports SQL authoring, data exploration, documentation search, and account administration. |
Focuses on question answering, data insights, and analysis-driven responses. |
Limited SQL and UI assistance. |
Key capabilities |
Generates and modifies SQL code, reviews changes using a diff view, and explains existing code. |
Analyzes data, generates summaries, and assists with natural language interactions. |
Contextual SQL suggestions and limited help features. |
Design focus |
Provides a unified AI interface across coding, documentation, and administrative workflows. |
Delivers conversational insights and query assistance for data understanding. |
Deprecated in favor of Cortex Code. |