Dynamic tables¶
Dynamic tables are tables that automatically refresh based on a defined query and target freshness, simplifying data transformation and pipeline management without requiring manual updates or custom scheduling.
When you create a dynamic table, you define a query that specifies how data should be transformed from base objects. Snowflake handles the refresh schedule of the dynamic table and updates the table automatically to reflect the changes made to the base objects based on the query.
Key considerations and general best practices¶
Immutability constraints: Use immutability constraints to let you control dynamic table updates. The constraints keep specific rows static while enabling incremental updates to the rest of the table. They prevent unwanted changes to marked data while they let normal refreshes occur for other parts of the table. For more information, see Use immutability constraints on dynamic tables.
Performance considerations: Dynamic tables use incremental processing for workloads that support it, which can improve performance by recomputing only the data that has changed, rather than performing a full refresh. For more information, see Best practices for optimizing dynamic table performance.
Break down complex dynamic tables: Break your pipeline into smaller, focused dynamic tables to improve performance and simplify troubleshooting. For more information, see Best practices for creating dynamic tables.
How dynamic tables work¶
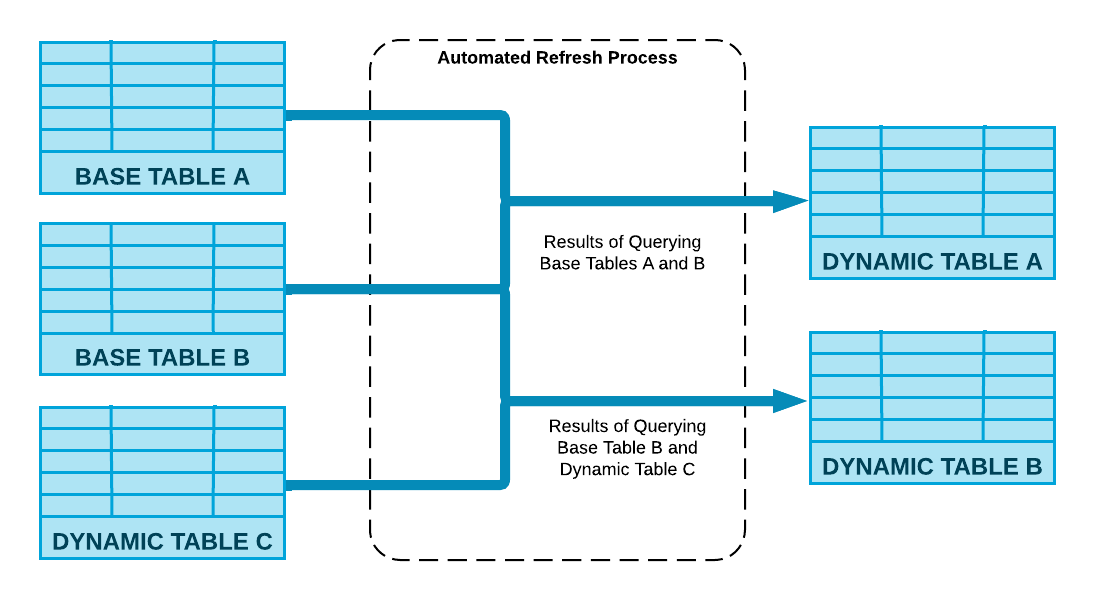
Snowflake runs the definition query specified in your CREATE DYNAMIC TABLE statement and your dynamic tables are updated through an automated refresh process.
The following diagram shows how this process computes the changes made to the base objects and merges them into the dynamic table by using compute resources associated with the table.
Target lag¶
Use target lag to set how fresh you want your data to be. Usually, the table data freshness won’t be more than that far behind the base table data freshness. With target lag, you control how often the table refreshes and how up-to-date the data stays.
For more information, see Understanding dynamic table target lag.
Dynamic table refresh¶
Dynamic tables aim to refresh within the target lag you specify. For example, a target lag of five minutes ensures that the data in the dynamic table is no more than five minutes behind data updates to the base table. You set the refresh mode when you create the table and, afterward, refreshes can happen on a schedule or manually.
For more information, see Understanding dynamic table initialization and refresh and Manually refresh dynamic tables.
When to use dynamic tables¶
Dynamic tables are ideal for the following scenarios:
You want to materialize query results without writing custom code.
You want to avoid manually tracking data dependencies and managing refresh schedules. Dynamic tables enable you to define pipeline outcomes declaratively, without managing transformation steps manually.
You want to chain together multiple tables for data transformations in a pipeline.
You don’t need fine-grained control over refresh schedules, and you only need to specify a target freshness for the pipeline. Snowflake handles the orchestration of data refreshes, including scheduling and execution, based on your target freshness requirements.
Example use cases¶
Slowly changing dimensions (SCDs): Dynamic tables can be used to implement Type 1 and Type 2 SCDs by reading from a change stream and using window functions over per-record keys ordered by a change timestamp. This method handles insertions, deletions, and updates that occur out of order, simplifying the creation of SCDs. For more information, see Slowly Changing Dimensions with Dynamic Tables.
Joins and aggregations: You can use dynamic tables to incrementally precompute slow joins and aggregations to enable fast queries.
Batch to streaming transitions: Dynamic tables support seamless transitions from batch to streaming with a single ALTER DYNAMIC TABLE command. You can control the refresh frequency in your pipeline to balance cost and data freshness.