Understanding and viewing Fail-safe¶
Separate and distinct from Time Travel, Fail-safe ensures historical data is protected in the event of a system failure or other event (e.g. a security breach).
What is Fail-safe?¶
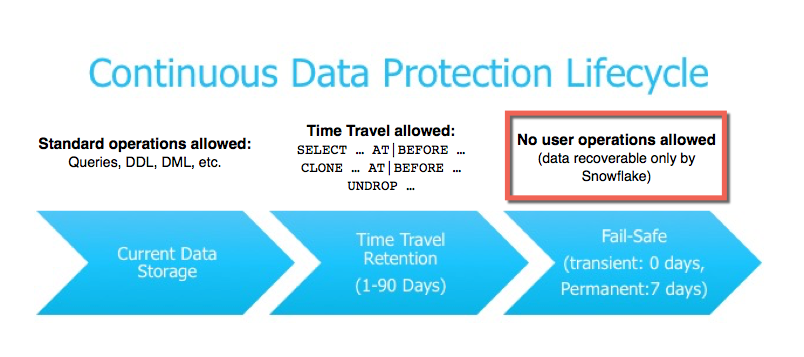
Fail-safe provides a (non-configurable) 7-day period during which historical data may be recoverable by Snowflake. This period starts immediately after the Time Travel retention period ends. Note, however, that a long-running Time Travel query will delay moving any data and objects (tables, schemas, and databases) in the account into Fail-safe, until the query completes.
Attention
Fail-safe is a data recovery service that is provided on a best effort basis and is intended only for use when all other recovery options have been attempted.
Fail-safe is not provided as a means for accessing historical data after the Time Travel retention period has ended. It is for use only by Snowflake to recover data that may have been lost or damaged due to extreme operational failures.
Data recovery through Fail-safe may take from several hours to several days to complete.
View Fail-safe storage for your account¶
When you review the total data storage usage for your account in Snowsight, you can view the historical data storage in Fail-safe.
You must use the ACCOUNTADMIN role to view the amount of data that is stored in Snowflake.
In Snowsight, follow these steps:
In the navigation menu, select Admin » Cost management, and then select Consumption.
Use the Usage Type filter to select Storage.
Review the graph and table for Fail-safe storage. The Storage Breakdown column in the table uses color-coded bars to represent the different kinds of storage, including Fail-safe storage. Hover the mouse pointer over each bar to see the size for each kind of storage.
Billing for Fail-safe¶
Data recovery through Fail-safe uses Snowflake-managed serverless compute. Standard serverless compute billing applies. For billing details, see “Table 5: Serverless Feature Table” in the Snowflake Service Consumption Table. To view the related credits that are consumed by data recovery through Fail-safe, use the following metering history views. Filter for the FAILSAFE_RECOVERY service type:
Considerations¶
For fail-safe and Snowpipe Streaming Classic, be aware of the following limitations:
Fail-safe doesn’t support tables that contain data ingested by Snowpipe Streaming Classic. For such tables, you can’t use fail-safe for recovery because fail-safe operations on that table will fail completely. For more information, see Snowpipe Streaming limitations.