OAuth authentication: Change in network policy behavior (Postponed)¶
Note
This behavior change was part of the 2025_06 bundle, but the change has been postponed. The change will be introduced in a future bundle. The change is not available for testing.
When this behavior change is enabled, there are changes to both Snowflake OAuth and External OAuth in how Snowflake enforces network policies to restrict incoming traffic from clients and end users.
Snowflake OAuth authentication: Change in the network policy used for a request from client to Snowflake¶
Snowflake OAuth lets you use a network policy to restrict network traffic from the OAuth client and from the user who is authenticating. There can be three different network policies restricting this traffic:
A network policy controlling requests from the OAuth client. This network policy is associated with the security integration that allows the client to interact with Snowflake.
A network policy controlling requests from the user who is authenticating. This network policy is associated with the user.
An account-level network policy that governs when there isn’t an integration-level or user-level network policy.
This behavior change affects which network policy governs a request from the OAuth client to Snowflake. The following diagram highlights the request that is affected by the change:
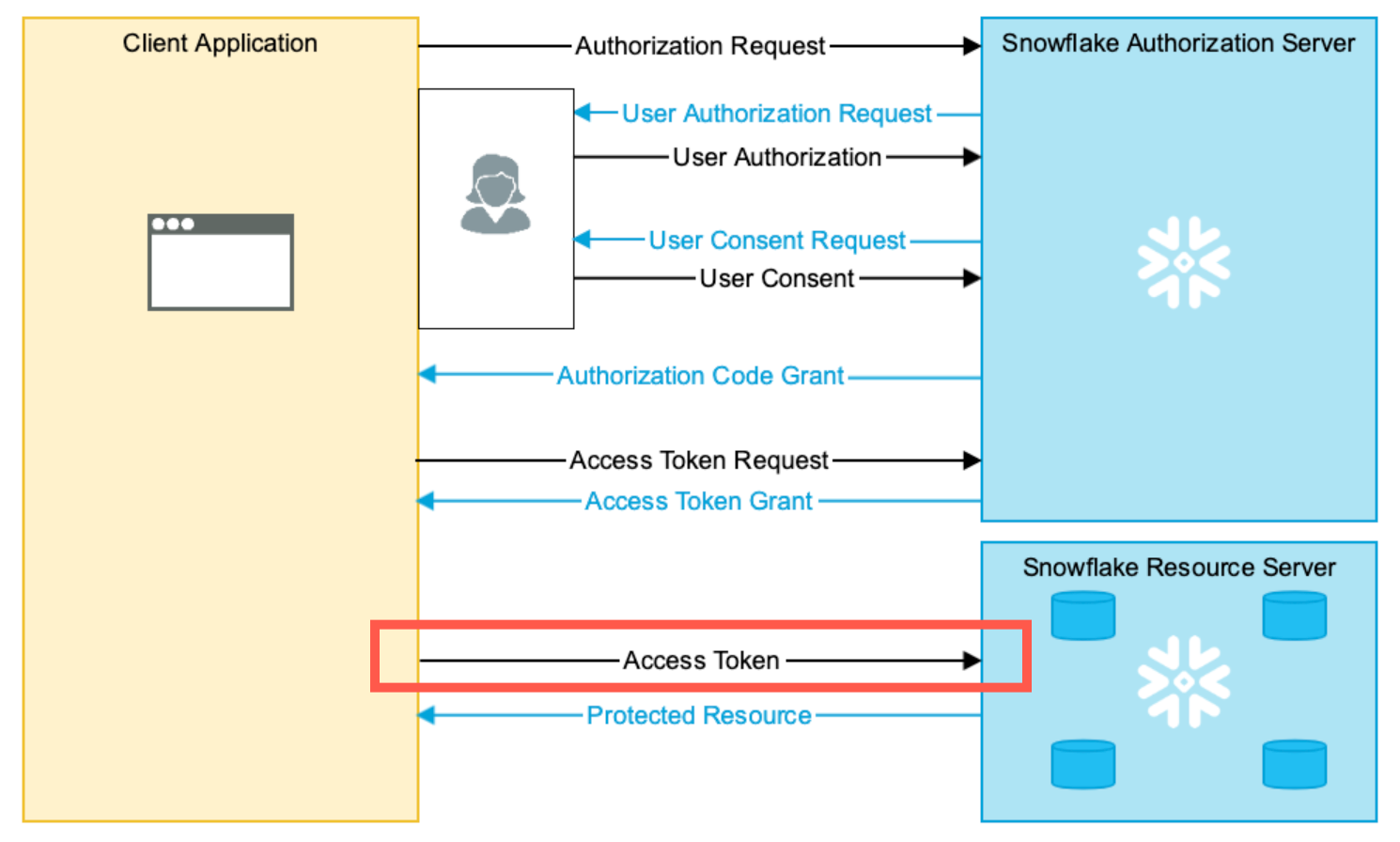
- Before the change:
The user-level network policy, not the integration-level network policy, governs a request that sends an access token from the OAuth client to Snowflake as the Resource Server.
- After the change:
The integration-level network policy, if specified, governs a request that sends an access token from the OAuth client to Snowflake as the Resource Server. If there is no integration-level network policy, the account-level network policy governs.
The network policies that govern other requests to Snowflake have not changed:
User authorization and user consent requests sent from the user to Snowflake are still governed by the user-level network policy, if specified.
The access token request sent from the OAuth client to Snowflake is still governed by the integration-level network policy, if specified.
External OAuth: Integration-level network policy takes precedence¶
When this bundle is enabled, you’ll be able to associate a network policy with an External OAuth security integration. Previously, only a Snowflake OAuth security integration could be associated with a network policy.
As part of this change, Snowflake will no longer consider user-level network policies when restricting network traffic from the OAuth client. Snowflake will enforce this change incrementally according to the following schedule:
When the change is Enabled by Default, Snowflake considers the user-level network policy and the integration-level network policy when restricting requests from the OAuth client.
To avoid failures during this period, attach the current user-level network policy to the security integration. The following code shows you how to determine the network policy that is assigned to the user, and then assign that same policy to the integration.
Find the network policy attached to the user:
SHOW PARAMETERS LIKE 'network_policy' IN USER <user_name>;
Attach the network policy returned by the preceding command to the External OAuth security integration:
ALTER SECURITY INTEGRATION <external_oauth_integration_name> SET NETWORK_POLICY = <network_policy_attached_to_user>;
When the change is Generally Enabled, a user-level network policy has no effect on requests from the OAuth client to Snowflake. Snowflake checks these requests against the integration-level network policy, then checks the account-level policy. Because the user-level network policy has no effect, you should remove it from the user by running the following command:
ALTER USER <user_name> UNSET NETWORK_POLICY;
Ref: 2094