Using the SMA AI assistant¶
You can use the SMA AI assistant to analyze and answer questions based exclusively on assessment data and documentation produced during the SMA migration assessment process.
How the assistant works¶
The assistant works on top of the assessment reports generated by the SMA (Snowflake Migration Accelerator). The process is divided into four main phases:
Activation
Processing questions and generating SQL
Retrieving answers
Formatting and delivering response
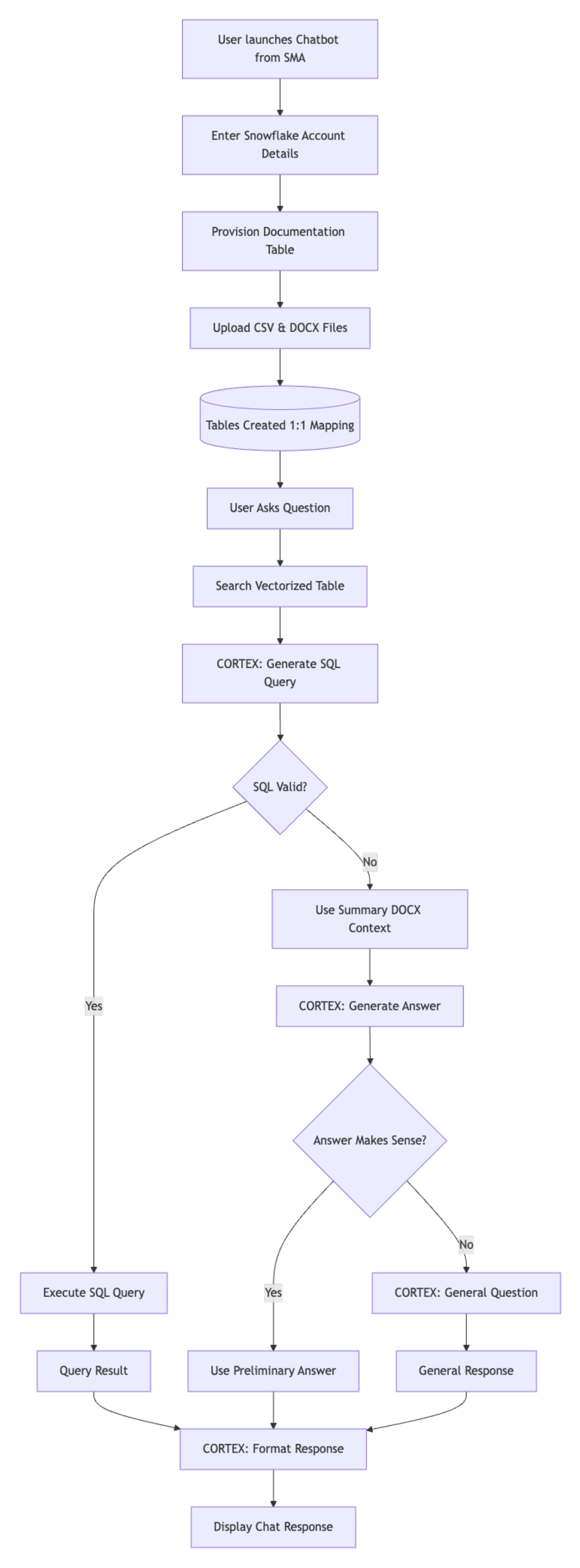
Phase 1: Activation and data ingestion¶
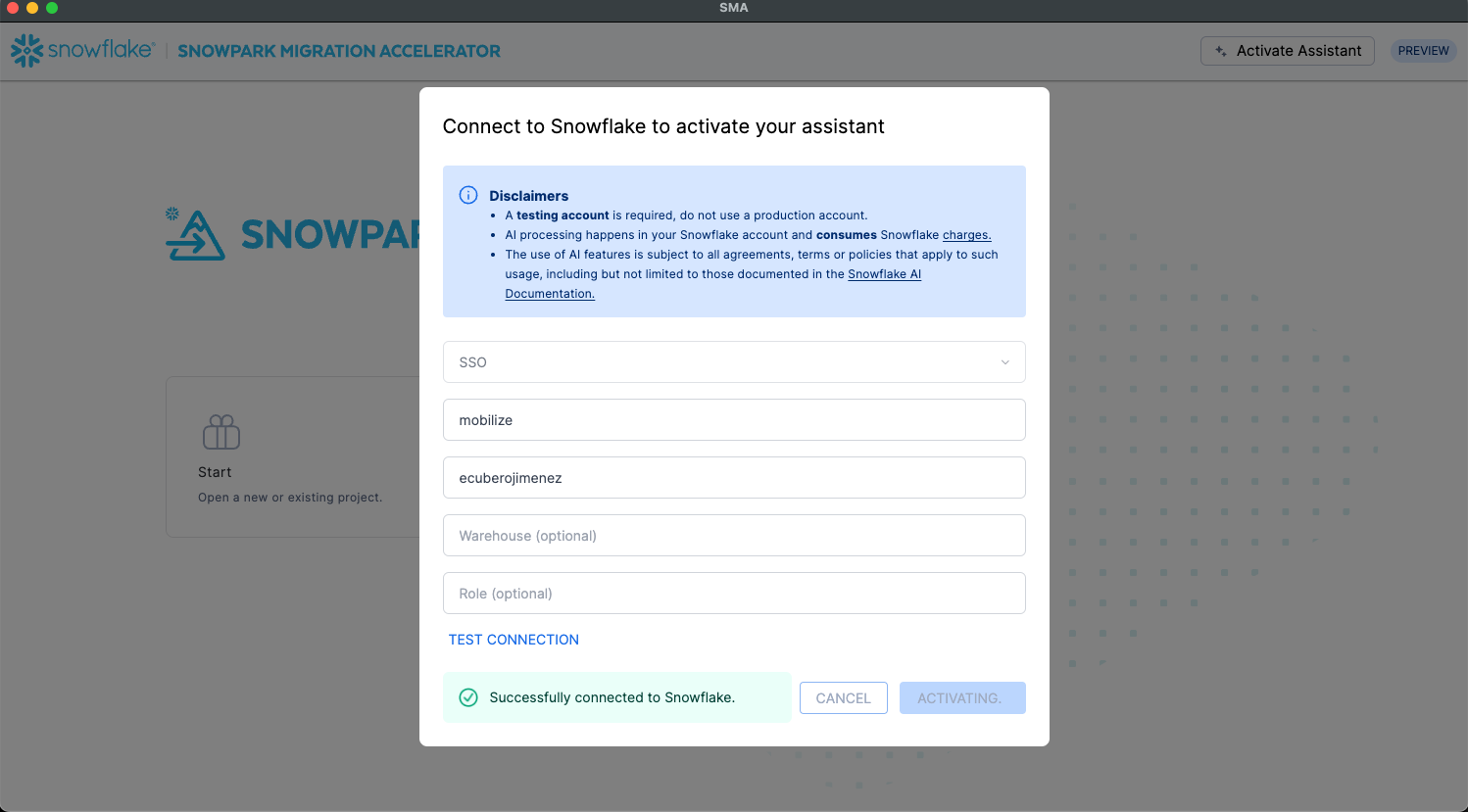
Activate the assistant.
The assistant is launched directly from the SMA application. Upon launch, you’ll be prompted to enter your Snowflake account credentials.
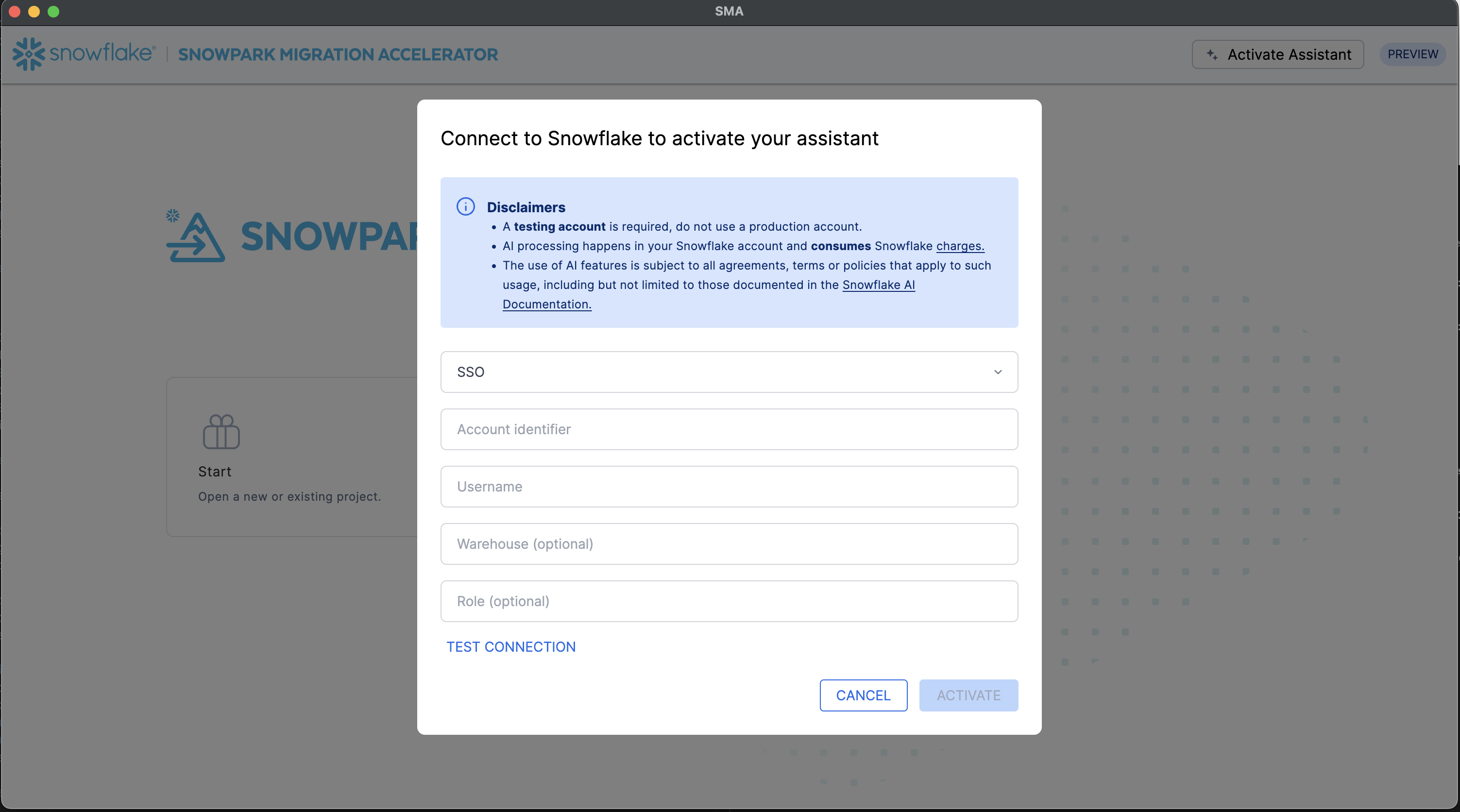
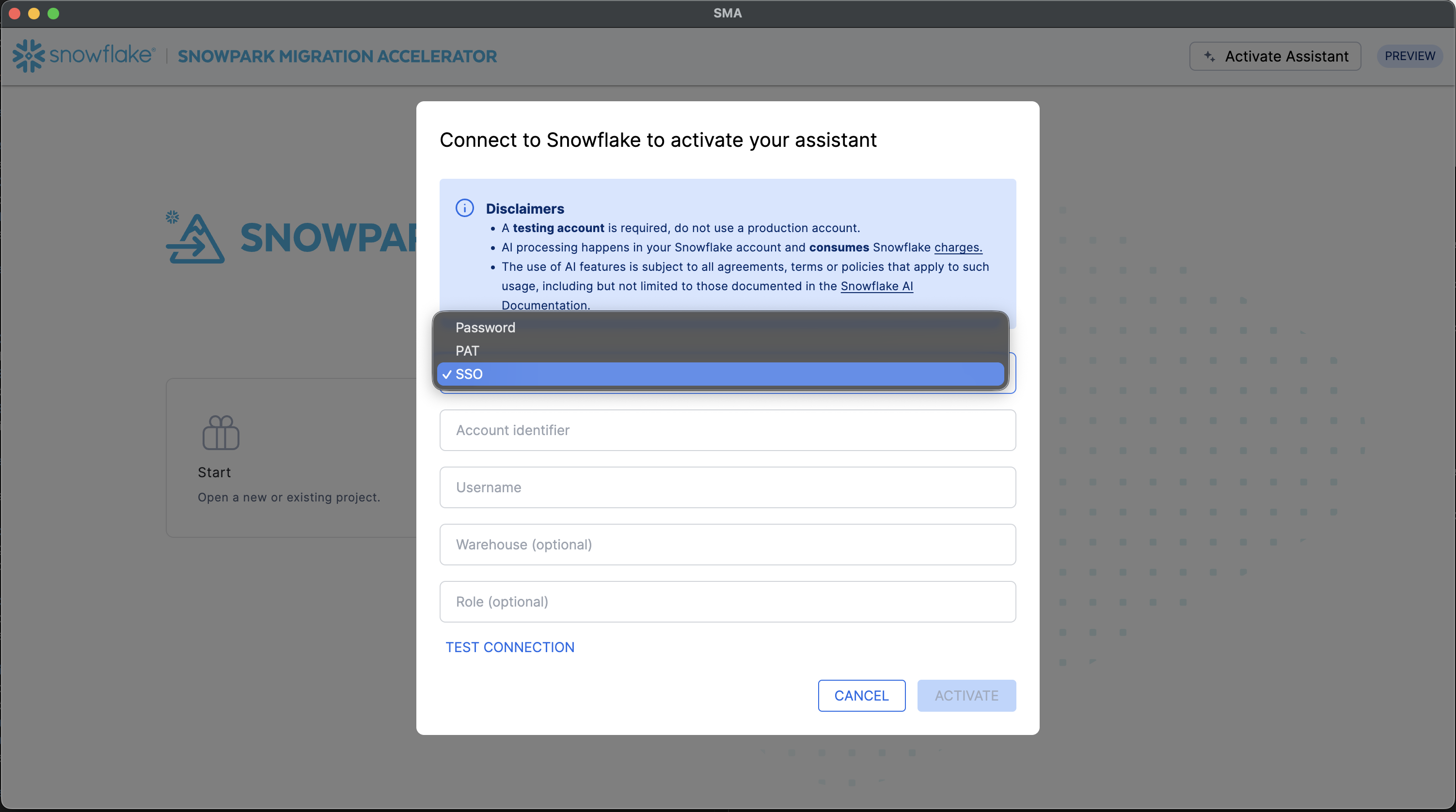
Configure authentication.
Select the appropriate authentication method for connecting to the Snowflake account. The assistant supports multiple authentication types to accommodate different security requirements.
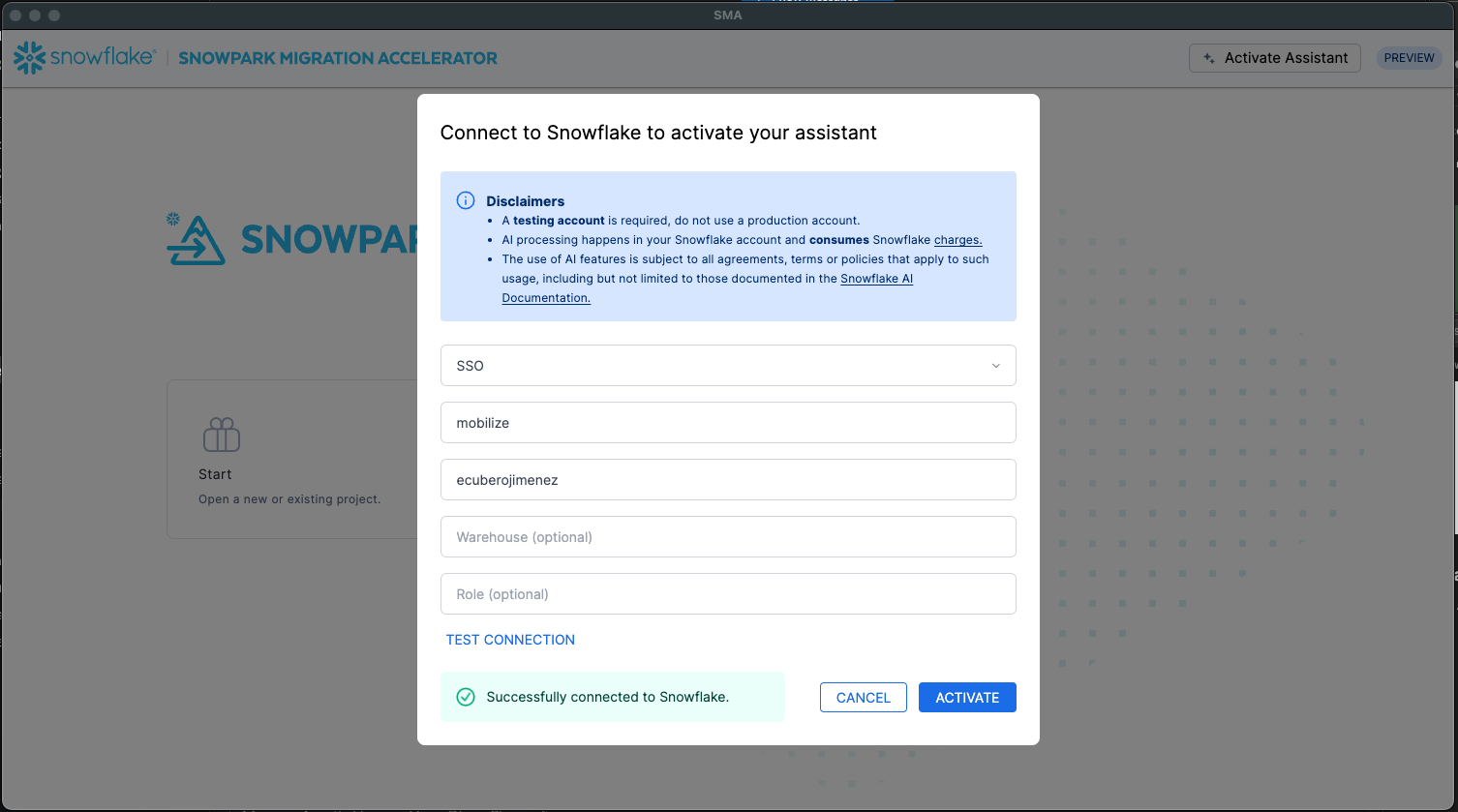
Test the connection.
Before proceeding, test the connection to ensure proper access to the Snowflake account. A successful connection test is required to activate the assistant, which then creates the necessary infrastructure (tables, schemas, etc.) in your Snowflake environment.
Provision infrastructure.
Once the connection is validated, the assistant automatically provisions a dedicated table structure within your Snowflake account for storing and managing documentation.
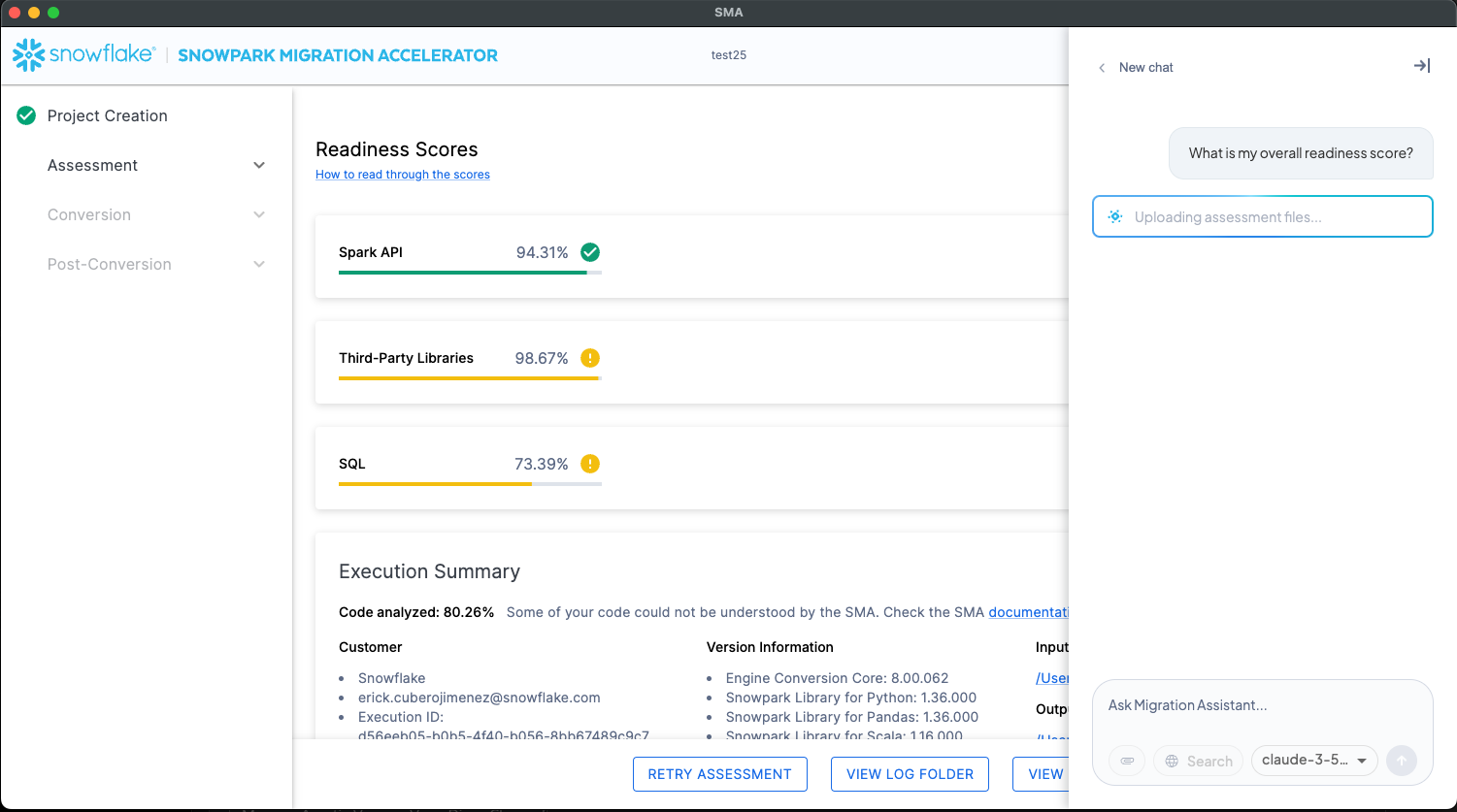
Ingest assessment data.
Upload all relevant assessment reports generated by the SMA. The assistant accepts both .csv and .docx files. Each uploaded file is mapped to a separate table in Snowflake, maintaining a one-to-one relationship between source files and database tables.
Phase 2: Question processing and SQL generation (RAG)¶
Once the infrastructure is ready, you can begin asking questions through the chat interface. Each question triggers a sophisticated retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) process powered by Snowflake Cortex.
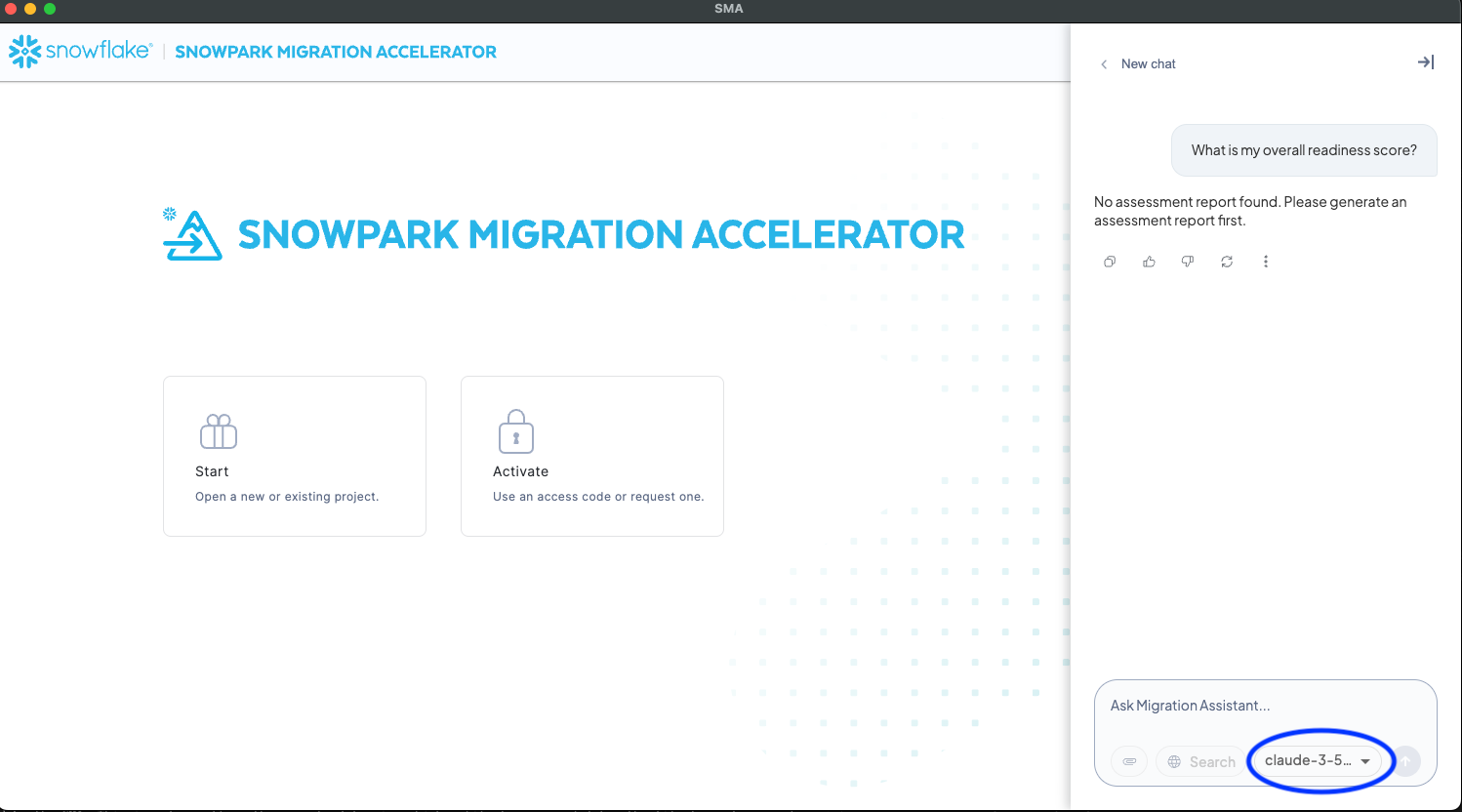
LLM selection¶
The assistant interface allows you to select from different Large Language Models (LLMs) to power the question-answering process. The available LLM options vary depending on the region where your Snowflake account is hosted, as Snowflake Cortex model availability differs across geographic regions.
Note
The list of available models is dynamically populated based on your Snowflake account’s region. Some advanced models might only be available in specific regions due to Snowflake’s regional deployment of Snowflake Cortex AI services.
Semantic documentation search
The assistant performs a semantic search against a vectorized documentation table in the Snowflake account to identify most relevant documents and data sources that can potentially answer your query.
Context-aware SQL generation
Using the identified documentation as context, Snowflake Cortex generates a targeted SQL query designed to extract the precise information needed to answer your question.
SQL validation (self-correction loop 1)
The generated SQL query undergoes validation by passing it back to Snowflake Cortex along with the original question to ensure the query logically produces an answer that addresses the user’s intent.
Phase 3: Answer retrieval and refinement¶
The answer retrieval process adapts based on the SQL validation results, ensuring the most accurate response possible.
The following scenarios describe what might happen.
Scenario A: Valid SQL query¶
The validated SQL query is executed against the assessment data tables.
The query results are extracted and prepared as the preliminary answer.
Scenario B: Invalid or insufficient SQL query¶
When SQL generation is not viable, the assistant falls back to the summary .docx file as context.
Snowflake Cortex generates a preliminary answer based on the documentation content rather than structured data.
Final answer verification (self-correction loop 2)¶
Before presenting the answer, the assistant performs a final quality check:
The preliminary answer is evaluated by Snowflake Cortex to verify it logically addresses the original question.
If validated: The answer is accepted and moves to formatting.
If not validated: The question is posed directly to Snowflake Cortex as a general inquiry (without specific documentation context), and this response becomes the final answer.
Phase 4: Response formatting and delivery¶
Natural language formatting¶
The final answer is processed one last time by Snowflake Cortex to transform it into a clear, conversational response that’s easy to understand and properly formatted for the chat interface.
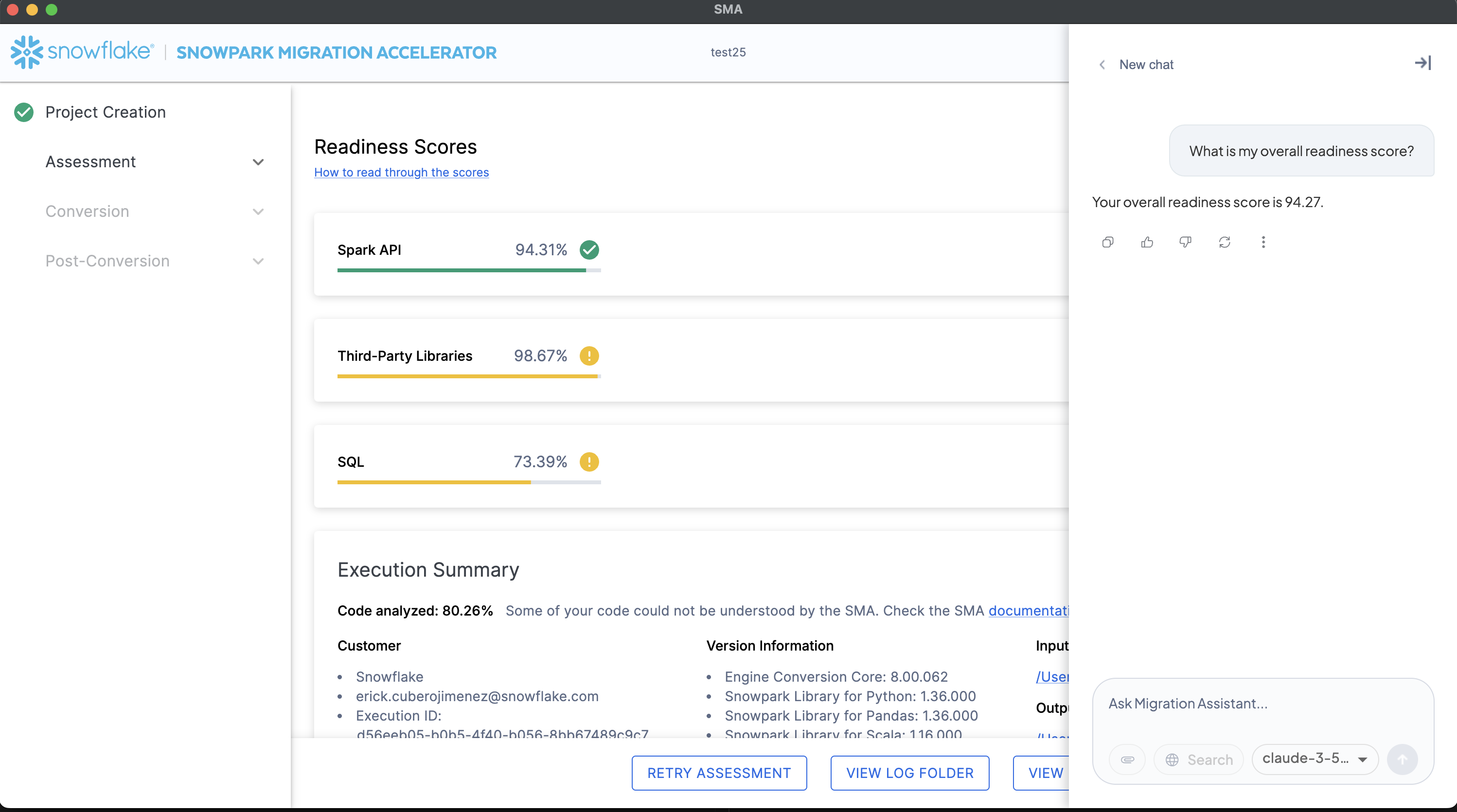
The formatted response is then displayed in the chat window, complete with proper structure, context, and any relevant details extracted from the assessment data.
Assessment report files and artifacts¶
The following files are uploaded to your account and serve as the data sources for the assistant:
File Type |
File Name |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
CSV |
|
Lists Databricks (DBX) elements found inside notebooks. |
CSV |
|
Lists the relations between different workload scopes based on function calls. |
CSV |
|
Lists generated checkpoints for the user workload. |
CSV |
|
Lists the DataFrames assignments found for generating checkpoints. |
CSV |
|
Lists the artifact dependencies of each file analyzed by the SMA. |
CSV |
|
Inventory of each file’s type and size present in that execution. |
CSV |
|
Lists all referenced import calls in the codebase. |
CSV |
|
Lists every file by filetype and size. |
CSV |
|
Lists all external elements being read from or written to. |
CSV |
|
Lists every conversion issue found, including description and location. |
CSV |
|
Inventory of all DataFrame joins done in that codebase. |
CSV |
|
Inventory of all cells in a notebook. |
CSV |
|
Lists the size in lines of code of different source languages in notebook files. |
CSV |
|
Lists every reference to the Pandas API (Python Only). |
CSV |
|
Shows the exact location and usage for each reference to the Spark API. |
CSV |
|
Count of SQL keywords present in SQL Spark elements. |
CSV |
|
Count of SQL elements present in SQL Spark elements. |
CSV |
|
Count of embedded SQL present in SQL Spark elements. |
CSV |
|
Lists the third-party references in the codebase. |
Database schema reference¶
This section describes the database tables created in your Snowflake account when using the assistant. These tables store migration assessment data, code inventories, and metadata used by the assistant to provide context-aware responses.
Schema overview¶
The assistant system creates tables to store:
Migration assessment data: Results from code analysis including dependencies, issues, and usage patterns
Code inventories: Detailed tracking of various code elements (imports, functions, DataFrames, etc.)
Documentation metadata: Vector embeddings for semantic search capabilities
Execution tracking: Records of tool executions and their results
Most tables include an EXECUTIONID column to associate records with specific migration assessment runs.
Table reference¶
DOCUMENTATION_METADATA¶
Stores documentation text with vector embeddings for semantic search capabilities. Used by the assistant to find relevant context based on user questions using vector similarity.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
TABLE_NAME |
VARCHAR |
Name of the table the documentation describes |
DOCUMENTATION_TEXT |
VARCHAR |
The documentation text content |
EMBEDDING |
VECTOR(FLOAT, 768) |
Vector embedding for semantic search |
ARTIFACTDEPENDENCYINVENTORIES¶
Lists the artifact dependencies of each file analyzed by the SMA. This inventory allows the user to determine which artifacts are needed for the file to work properly in Snowflake.
The following are considered artifacts: a third-party library, SQL entity, source of a read or write operation, and another source code file in the workload.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The identifier of the execution |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The identifier of the source code file |
DEPENDENCY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The artifact dependency that the current file has |
TYPE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The type of the artifact dependency |
SUCCESS |
BOOLEAN |
If the artifact needs any intervention, it shows FALSE; otherwise, it shows TRUE |
STATUSDETAIL |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The status of the artifact dependency, based on the type |
ARGUMENTS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Extra data of the artifact dependency, based on the type |
LOCATION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The collection of cell ID and line number where the artifact dependency is being used in the source code file |
INDIRECTDEPENDENCIES |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A list of other files that this file relies on, even if not directly |
TOTALINDIRECTDEPENDENCIES |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The total count of these indirect dependencies |
DIRECTPARENTS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A list of files that directly use this file |
TOTALDIRECTPARENTS |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The total count of these direct parent files |
INDIRECTPARENTS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A list of files that use this file indirectly (through other files) |
TOTALINDIRECTPARENTS |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The total count of these indirect parent files |
CHECKPOINTSINVENTORIES¶
Lists the generated checkpoints for the user workload. These checkpoints are completely capable of being used in the Checkpoints Feature from the Snowflake Extension.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
NAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The checkpoint name (using the format described before) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The relative path of the file (starting from the input folder the user chose in the SMA tool) |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of cell where the DataFrame operation was found inside a notebook file |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Line number where the DataFrame operation was found |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The column number where the DataFrame operation was found |
TYPECHECKPOINT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The use case of the checkpoints (Collection or Validation) |
DATAFRAMENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the DataFrame |
LOCATIONASSIGNMENT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The assignment number of the DataFrame name |
ENABLED |
BOOLEAN |
Indicates whether the checkpoint is enabled (True or False) |
MODENUMBER |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The mode number of the collection (Schema [1] or DataFrame [2]) |
SAMPLEDATAFRAME |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The sample of the DataFrame |
ENTRYPOINT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The entry point that guides the flow to execute the checkpoint |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The execution ID |
DATAFRAMESINVENTORIES¶
Lists the DataFrame assignments to use when generating checkpoints for the user workload
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
FULLNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The full name of the DataFrame |
NAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The simple name of the variable of the DataFrame |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The relative path of the file (starting from the input folder the user chose in the SMA tool) |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of cells where the DataFrame operation was found inside a notebook file |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number where the DataFrame operation was found |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The column number where the DataFrame operation was found |
ASSIGNMENTNUMBER |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of assignments for this particular identifier (not symbol) in the file |
RELEVANTFUNCTION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The relevant function why this was collected |
RELATEDDATAFRAMES |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The fully-qualified name of the DataFrame(s) involved in the operation (separated by semicolons) |
ENTRYPOINTS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Empty for this phase |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The execution ID |
DBXELEMENTSINVENTORIES¶
Lists the DBX (Databricks) elements found inside notebooks.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The DBX element name |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the element was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
CATEGORY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The element category |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A category for each element. These could include Function or Magic |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source files where the element was found |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the package where the element was found |
SUPPORTED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether this reference is “supported” or not ( |
AUTOMATED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether or not the tool can automatically convert it ( |
STATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The categorization of each element (Rename, Direct, Helper, Transformation, WorkAround, NotSupported, or NotDefined) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
SNOWCONVERTCOREVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version number for the core code process of the tool |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
If this element was found in a notebook file, the numbered location of the cell where this element was in the file |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique identifier for this execution of the SMA |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source technology platform |
DETAILEDREPORTS¶
Stores detailed migration assessment reports for each execution. Used by the assistant to provide context-specific answers about migration assessments.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Auto-incrementing primary key |
EXECUTION_ID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for the execution run |
REPORT_TEXT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Full text of the detailed report |
EXECUTIONFLOWINVENTORIES¶
Lists the relations between the different workload scopes, based on the function calls found. This inventory’s main purpose is to serve as the base for the entry points identification.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CALLER |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The full name of the scope where the call was found |
CALLERTYPE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The type of the scope where the call was found. This can be: Function, Class, or Module |
INVOKED |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The full name of the element that was called |
INVOKEDTYPE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The type of the element. This can be: Function or Class |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The relative path of the file (starting from the input folder the user chose in the SMA tool) |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The cell number where the call was found inside a notebook file, if applicable |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number where the call was found |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The column number where the call was found |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The execution ID |
IMPORTUSAGESINVENTORIES¶
Contains all the referenced import calls in the codebase. An import is classified as an external library that gets imported at any point in the file.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique name for the actual Spark reference |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
ALIAS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The alias of the element (if any) |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Null/empty value because all elements are imports |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source files where the element was found |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the package where the element was found |
ISSNOWPARKANACONDASUPPORTED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether this reference is “supported” or not. Values: |
AUTOMATED |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Null/empty. This column is deprecated |
STATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Value Invalid. This column is deprecated |
STATEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The code where the element was used. (Note: This column is not sent via telemetry) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
SNOWCONVERTCOREVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version number for the core code process of the tool |
SNOWPARKVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version of Snowpark API available for the specified technology and run of the tool |
ELEMENTPACKAGE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The package name where the imported element is declared (when available) |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
If this element was found in a notebook file, the numbered location of the cell where this element was in the file |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique identifier for this execution of the SMA |
ORIGIN |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Category of the import reference. Possible values are BuiltIn, ThirdPartyLib, or blank |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source technology platform |
FULLNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
It represents the correct full path for the current element |
INPUTFILESINVENTORIES¶
Similar to the files inventory, lists every file by filetype and size.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Filename (same as FileId) |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of files with that filename |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each session of the tool |
EXTENSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The file’s extension |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The source file’s technology based on extension |
BYTES |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Size of the file in bytes |
CHARACTERLENGTH |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of characters in the file |
LINESOFCODE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Lines of code in the file |
PARSERESULT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
“Successful” if the cell was fully parsed, “Error” if it was not parsed |
IGNORED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether file was ignored |
ORIGINFILEPATH |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Original file path |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique identifier for this execution of the SMA |
IOFILESINVENTORIES¶
Lists all external elements that are being read from or written to in the codebase.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The file, variable, or other element being read or written |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of files with that filename |
ISLITERAL |
BOOLEAN |
If the read/write location was in a literal |
FORMAT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
If the SMA can determine the format of the element (such as csv, json, etc.) |
FORMATTYPE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
If the format above is specific |
MODE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Value will be |
SUPPORTED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether this operation is supported in Snowpark |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line in the file where the read or write occurs |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each session of the tool |
OPTIONSETTINGS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
If a parameter is defined in the element, it will be listed here |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Cell ID where that element was in that FileId (if in a notebook, null otherwise) |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
ISSUES¶
Lists every conversion issue found in the codebase. A description, the exact location of the issue in the file, and a code associated with that issue will be reported.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CODE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique code for the issues reported by the tool |
DESCRIPTION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The text describing the issue and the name of the Spark reference when applies |
CATEGORY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The classification of each issue. Options: Warning, Conversion Error, Parser Error, Helper, Transformation, WorkAround, NotSupported, NotDefined |
NODETYPE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name associated to the syntax node where the issue was found |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source file where the issue was found |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The column position in the source file where the issue was found |
URL |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
URL to documentation or more info |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique identifier for this execution of the SMA |
JOINSINVENTORIES¶
Contains an inventory of all DataFrame joins done in the codebase.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Line number where the join begins (and ends, if not on a single line) |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of files with that filename |
ISSELFJOIN |
BOOLEAN |
TRUE if the join is a self join, FALSE if not |
HASLEFTALIAS |
BOOLEAN |
TRUE if the join has a left alias, FALSE if not |
HASRIGHTALIAS |
BOOLEAN |
TRUE if the join has a right alias, FALSE if not |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Line number where the join begins |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Join type (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, etc.) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each session of the tool |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Cell ID where that element was in that FileId (if in a notebook, null otherwise) |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
NOTEBOOKCELLSINVENTORIES¶
Gives an inventory of all cells in a notebook based on the source code for each cell and the lines of code in that cell.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source language (Python, Scala, or SQL) |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of files with that filename |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Cell ID where that element was in that FileId (if in a notebook, null otherwise) |
ARGUMENTS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Null (this field will be empty) |
LOC |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Lines of code in that cell |
SIZE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of characters in that cell |
SUPPORTEDSTATUS |
BOOLEAN |
|
PARSINGRESULT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
“Successful” if the cell was fully parsed; “Error” if it was not parsed |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
NOTEBOOKSIZEINVENTORIES¶
Lists the size in lines of code of different source languages present in notebook files.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Filename (for this spreadsheet, it is the same as the FileId) |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Count of files with that filename |
PYTHONLOC |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Python lines of code present in notebook cells (will be 0 for non-notebook files) |
SCALALOC |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Scala lines of code present in notebook cells (will be 0 for non-notebook files) |
SQLLOC |
NUMBER(38,0) |
SQL lines of code present in notebook cells (will be 0 for non-notebook files) |
LINE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Null (this field will be empty) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each session of the tool |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
PACKAGESINVENTORIES¶
Tracks package usage in the codebase.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the package |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where package was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
ALIAS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Package alias if used |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Type of package |
LINE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Line reference |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Full package name |
SUPPORTED |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Support status |
AUTOMATED |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Automation status |
STATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Migration status |
STATEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Full import statement |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Session identifier |
SNOWCONVERTCOREVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
SnowConvert core version used |
SNOWPARKVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Target Snowpark version |
CELLID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Cell identifier (for notebooks) |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
PARAMETERSINFO |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Parameter information |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source technology platform |
PANDASUSAGESINVENTORIES¶
[Python Only] Lists every reference to the Pandas API present in the scanned codebase.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique name for the actual pandas reference |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
ALIAS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The alias of the element (applies just for import elements) |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A category for each element. These could include Class, Variable, Function, Import and others |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source files where the element was found |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the package where the element was found |
SUPPORTED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether this reference is “supported” or not. Values: |
AUTOMATED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether or not the tool can automatically convert it. Values: |
STATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The categorization of each element. Options: Rename, Direct, Helper, Transformation, WorkAround, NotSupported, NotDefined |
STATEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
How that element was used. (Note: This column is not sent via telemetry) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
SNOWCONVERTCOREVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version number for the core code process of the tool |
PANDASVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Version number of the pandas API that was used to identify elements in this codebase |
CELLID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Cell ID where that element was in that FileId (if in a notebook, null otherwise) |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
PARAMETERSINFO |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Parameter information |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source technology platform |
SPARKUSAGESINVENTORIES¶
Shows the exact location and usage for each reference to the Spark API. This information is used to build the Readiness Score.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique name for the actual Spark reference |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
ALIAS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The alias of the element (applies just for import elements) |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
A category for each element. These could include Class, Variable, Function, Import and others |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source files where the element was found |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the package where the element was found |
SUPPORTED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether this reference is “supported” or not. Values: |
AUTOMATED |
BOOLEAN |
Whether or not the tool can automatically convert it. Values: |
STATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The categorization of each element. Options: Rename, Direct, Helper, Transformation, WorkAround, NotSupported, NotDefined |
STATEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The code where the element was used. (Note: This column is not sent via telemetry) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
SNOWCONVERTCOREVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version number for the core code process of the tool |
SNOWPARKVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version of Snowpark API available for the specified technology and run of the tool |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
If this element was found in a notebook file, the numbered location of the cell where this element was in the file |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique identifier for this execution of the SMA |
PARAMETERSINFO |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Parameter information |
TECHNOLOGY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Source technology platform |
SQLEMBEDDEDUSAGEINVENTORIES¶
Contains a count of SQL keywords present in SQL Spark elements.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name for the code element where the SQL was found (such as SqlFromClause, SqlSelect, SqlSelectBody, SqlSignedNumericLiteral) |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the SQL reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
LIBRARYNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the library being used |
HASLITERAL |
BOOLEAN |
Indicates whether the element contains literals |
HASVARIABLE |
BOOLEAN |
Indicates whether the element contains variables |
HASFUNCTION |
BOOLEAN |
Indicates whether the element contains functions |
PARSINGSTATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Indicates the parsing status (such as Success, Failed, Partial) |
HASINTERPOLATION |
BOOLEAN |
Indicates whether the element contains interpolations |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The notebook cell ID |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number where that element occurs |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The column number where that element occurs |
SQLFUNCTIONSINVENTORIES¶
Inventories SQL functions used in the code with their categories and migration status.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
SQL function name |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Project identifier |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Identifier for the source file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Number of occurrences |
CATEGORY |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Function category |
MIGRATIONSTATUS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Migration status for this function |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Cell identifier (for notebooks) |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Line number in the source file |
COLUMNLINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Column position in the line |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for the execution run |
THIRDPARTYUSAGESINVENTORIES¶
Tracks third-party library and package usage found during code analysis.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The unique name for the third party reference |
PROJECTID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Name of the project (root directory the tool was run on) |
FILEID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
File where the Spark reference was found and the relative path to that file |
COUNT |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The number of times that element shows up in a single line |
ALIAS |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The alias of the element (if any) |
KIND |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Categorization of the element such as variable, type, function, or class |
LINE |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The line number in the source files where the element was found |
PACKAGENAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Package name for the element (concatenation of ProjectId and FileId in Python) |
STATEMENT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The code where the element was used. (Note: This column is not sent via telemetry) |
SESSIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each session of the tool |
CELLID |
NUMBER(38,0) |
Cell ID where that element was in that FileId (if in a notebook, null otherwise) |
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each execution of the tool |
PARAMETERSINFO |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Parameter information |
TOOLEXECUTIONS¶
Tracks tool execution metadata including timing, results, and version information.
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
EXECUTIONID |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Unique identifier for each run of the tool |
TOOLNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the tool. Values: PythonSnowConvert, SparkSnowConvert (Scala tool) |
TOOLVERSION |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The version number of the tool |
ASSEMBLYNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The name of the code processor (essentially, a longer version of the ToolName) |
LOGFILE |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Whether a log file was sent on an exception/failure |
FINALRESULT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
Where the tool stopped if there was an exception/failure |
EXCEPTIONREPORT |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
If an exception report was sent on an exception/failure |
STARTTIME |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The timestamp for when the tool started executing |
ENDTIME |
NUMBER(38,0) |
The timestamp for when the tool stopped executing |
SYSTEMNAME |
VARCHAR(16777216) |
The serial number of the machine where the tool was executing (this is only used for troubleshooting and license validation purposes) |
Assessment files to table mapping¶
The following CSV files from assessment exports map to their corresponding database tables:
CSV File |
Database Table |
|---|---|
ArtifactDependencyInventory.csv |
ARTIFACTDEPENDENCYINVENTORIES |
CheckpointsInventory.csv |
CHECKPOINTSINVENTORIES |
DataFramesInventory.csv |
DATAFRAMESINVENTORIES |
DbxElementsInventory.csv |
DBXELEMENTSINVENTORIES |
ExecutionFlowInventory.csv |
EXECUTIONFLOWINVENTORIES |
ImportUsagesInventory.csv |
IMPORTUSAGESINVENTORIES |
InputFilesInventory.csv |
INPUTFILESINVENTORIES |
IOFilesInventory.csv |
IOFILESINVENTORIES |
Issues.csv |
ISSUES |
JoinsInventory.csv |
JOINSINVENTORIES |
NotebookCellsInventory.csv |
NOTEBOOKCELLSINVENTORIES |
NotebookSizeInventory.csv |
NOTEBOOKSIZEINVENTORIES |
PackagesInventory.csv |
PACKAGESINVENTORIES |
PandasUsagesInventory.csv |
PANDASUSAGESINVENTORIES |
SparkUsagesInventory.csv |
SPARKUSAGESINVENTORIES |
SqlEmbeddedUsageInventory.csv |
SQLEMBEDDEDUSAGEINVENTORIES |
SqlFunctionsInventory.csv |
SQLFUNCTIONSINVENTORIES |
ThirdPartyUsagesInventory.csv |
THIRDPARTYUSAGESINVENTORIES |
tool_execution.csv |
TOOLEXECUTIONS |
DetailedReport.docx |
DETAILEDREPORTS |
Schema notes¶
The
DOCUMENTATION_METADATAtable uses vector embeddings (768 dimensions) for semantic search.Tables are created with
CREATE OR REPLACEto ensure clean setup on each initialization.
Stored procedures¶
The assistant creates several stored procedures in your Snowflake account to power the natural language query processing capabilities. These procedures leverage Snowflake Cortex AI to interpret questions, generate SQL, and format responses.
GET_CHATBOT_RESPONSE¶
The primary stored procedure that processes natural language questions and returns human-readable answers using Snowflake Cortex AI.
Signature¶
Parameters¶
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
IA_MODEL |
VARCHAR |
The Snowflake Cortex AI model to use (such as ‘llama3.1-70b’, ‘mistral-large2’) |
QUESTION |
VARCHAR |
The natural language question from the user |
EXECUTION_ID |
VARCHAR |
The execution ID to filter data to a specific assessment run |
Returns¶
VARCHAR - A human-readable answer to the user’s question
Workflow¶
The procedure implements a multi-step process:
Context Retrieval (RAG)
Performs vector similarity search on
DOCUMENTATION_METADATAtable.Uses
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.EMBED_TEXT_768with the ‘e5-base-v2’ model.Retrieves the most relevant documentation using
VECTOR_COSINE_SIMILARITY.
SQL Generation
Constructs a prompt with the retrieved context and user question.
Calls
SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COMPLETEto generate a SQL query.The generated query is scoped to the specific
EXECUTION_ID.
SQL Validation (Self-Correction Loop 1)
Validates whether the generated SQL logically answers the question.
Uses Snowflake Cortex to perform a yes/no validation check.
Fallback Path (if SQL is invalid)
Retrieves full report context from
DETAILEDREPORTStable.Attempts to answer using the detailed report as context.
Performs another validation check on the answer quality.
Falls back to general knowledge if context-based answer is insufficient.
SQL Execution (if SQL is valid)
Executes the generated SQL query dynamically.
Stores results in a temporary table for processing.
Handles single results, multiple results (aggregates up to 10), and empty results.
Response Formatting
Creates a final prompt combining the question and query results.
Calls Snowflake Cortex again to format the answer as a friendly, natural sentence.
Returns the human-readable response.
Error Handling¶
Returns
"I could not find any data that matched your request."when query returns zero rows.Automatically falls back through multiple strategies to ensure a meaningful answer.
Example¶
GET_CURRENT_REGION_DETAILS¶
Retrieves information about the current Snowflake account’s region, including cloud provider and region display name.
Signature¶
Parameters¶
None
Returns¶
A table with three columns:
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CLOUD_PROVIDER |
VARCHAR |
The cloud provider (such as ‘AWS’, ‘Azure’, ‘GCP’) |
CLOUD_REGION_NAME |
VARCHAR |
The technical region identifier (such as ‘us-east-1’) |
CLOUD_REGION_DISPLAY_NAME |
VARCHAR |
The human-readable region name (such as ‘US East (N. Virginia)’) |
Workflow¶
Executes
SHOW REGIONSto populate the result set cache.Queries the result using
RESULT_SCAN(LAST_QUERY_ID()).Filters to only the region matching
CURRENT_REGION().Returns the filtered result as a table.
Purpose¶
This procedure is used to determine which Snowflake Cortex AI models are available, as model availability varies by region. The assistant uses this information to populate the LLM selection dropdown with region-specific options.
Example¶
Output¶
CLOUD_PROVIDER |
CLOUD_REGION_NAME |
CLOUD_REGION_DISPLAY_NAME |
|---|---|---|
AWS |
us-west-2 |
US West (Oregon) |
Stored procedure notes¶
Both procedures are created with
CREATE OR REPLACEto ensure clean setup.GET_CHATBOT_RESPONSEexecutes asOWNERto access the necessary tables and Snowflake Cortex functions.The procedures use Snowflake’s dynamic SQL capabilities (
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE) for flexible query execution.Vector embeddings use the ‘e5-base-v2’ model with 768 dimensions for semantic search.
The multi-step validation process ensures high-quality, contextually relevant answers.
Troubleshooting¶
Resetting the assistant infrastructure¶
If you need to re-create the assistant infrastructure from scratch, you must first delete the local configuration file.
Configuration file location¶
macOS/Linux:
~/.smachatbot/config.jsonWindows:
%USERPROFILE%.smachatbotconfig.json
This JSON configuration file contains a composite key consisting of:
snowflake_identifiersnowflake_usersnowflake_role
To reset the assistant:
Delete the
config.jsonfile from the appropriate directory:macOS/Linux:
~/.smachatbot/config.jsonWindows:
%USERPROFILE%.smachatbotconfig.json
Re-run the assistant initialization process
Note
Deleting this file will remove all stored connection settings and require you to reconfigure the assistant with your Snowflake credentials.
Known issues / FAQs¶
Snowflake connection caching with VPN¶
Issue¶
When testing the connection to Snowflake while a VPN is required but not yet connected, the Snowflake driver caches the failed connection state. Even after successfully connecting to the VPN, subsequent connection attempts may still fail due to this cached state.
Workaround¶
If you experience connection failures after connecting to your VPN:
Close and restart the SMA application.
Attempt the connection test again with the VPN active from the start.
Tip
Always ensure your VPN is connected before initiating any Snowflake connection tests to avoid this caching behavior.