SnowConvert AI: Data migration¶
SnowConvert AI, as part of the end-to-end migration experience, provides the capability to migrate your actual data from source tables to Snowflake after the database structure is deployed. This data migration feature ensures that your data is transferred efficiently and accurately to complete the data migration process. This data migration feature is available for SQL Server and Amazon Redshift databases.
Data migration process overview¶
The data migration process varies depending on your source database platform.
Amazon Redshift to Snowflake¶
SnowConvert AI migrates data from Redshift tables by unloading it to PARQUET files in an S3 bucket, then copying the data directly from those files to the deployed tables in Snowflake.
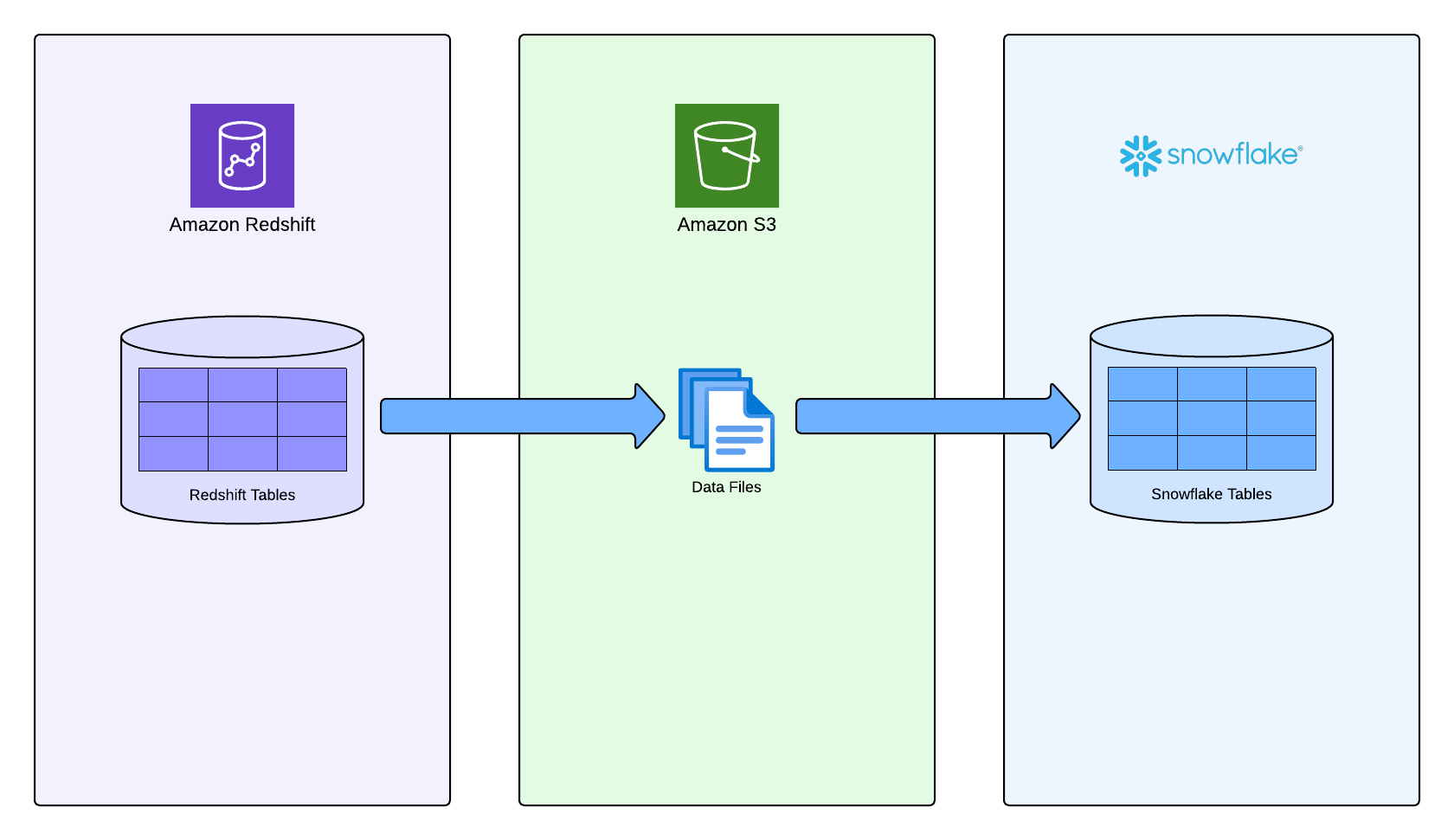
SQL Server to Snowflake¶
Data migration from SQL Server utilizes optimized data transfer methods to move your table data efficiently to the corresponding Snowflake tables.
Prerequisites¶
Ensure that you meet the following general prerequisites:
You completed the deployment process with database structure in Snowflake.
You have active connections to both a source database and Snowflake account.
You have sufficient permissions for data operations on both source and target systems.
In addition, ensure that the prerequisites are complete for your source database platform:
Prerequisites for Amazon Redshift sources¶
Before executing data migration from Redshift, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
S3 bucket requirements¶
An S3 bucket in AWS in the same region as your Redshift cluster.
Empty bucket path; the process fails if files exist in the specified path.
IAM role for Redshift¶
Create an IAM role associated with your Redshift cluster that can unload data to your S3 bucket:
IAM user for S3 access¶
Create an IAM user with permissions to read and delete objects from your S3 bucket:
Warning
If you don’t provide s3:DeleteObject and s3:DeleteObjectVersion permissions, the temporary data files won’t be deleted from the S3 bucket even if the migration succeeds.
Prerequisites for SQL Server sources¶
Valid connection to your SQL Server source database.
Appropriate permissions to read data from source tables.
Network connectivity between the migration tool and both source and target systems.
Migrate your data¶
Complete the end-to-end data migration process by transferring your actual data to the deployed database structure in Snowflake:
Migrate Amazon Redshift data¶
In SnowConvert AI, open the project, and then select Migrate data.
On the Connect to source database page, complete the fields with the connection information for your source database, and then select Continue.
On the Connect to Snowflake page, complete the fields with your connection information, and then select Continue.
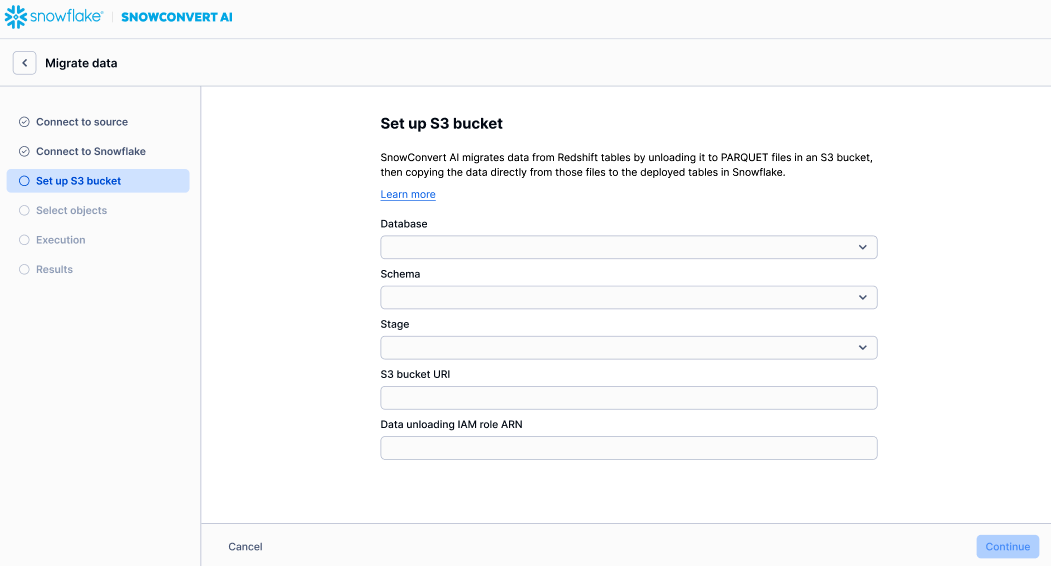
On the Set up S3 bucket page, specify the following information:
Database: Select the database that contains the tables that you want to migrate.
Schema: Select the schema that contains the tables that you want to migrate.
Stage: Select the stage where data files will be stored.
S3 bucket URI: Enter the Uniform Resource Identifier for the Amazon S3 bucket that contains the source data. The URL must end with
/.Data unloading IAM role ARN: Enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the IAM role that you used to unload the data to Amazon S3.
The following image is an example of the page:
Create a stage integration to S3¶
If you don’t have an existing stage configured, you need to create a Snowflake external stage that integrates with your S3 bucket. You can create the stage using the following SQL command in Snowflake:
Alternatively, if you’re using AWS credentials directly:
Replace the placeholders:
<stage_name>: Your desired stage name (for example,my_redshift_stage)<your_bucket_name>: Your S3 bucket name<path>: Optional path within the bucket<your_storage_integration>: Your Snowflake storage integration name (recommended method)<your_aws_key_id>and<your_aws_secret_key>: Your AWS IAM user credentials (if not using storage integration)
Note
Using a Snowflake storage integration is the recommended approach for better security and credential management. For more information about creating storage integrations, see the Snowflake documentation.
Verify stage integration¶
After setting up your stage, verify that the integration is working correctly before proceeding with data migration. You can verify the stage integration by running the following command in Snowflake:
This command should execute successfully without errors. If the stage is newly created and empty, it may return no results, which is expected.
To perform a more thorough verification, you can test the stage by uploading a test file:
If the commands execute successfully and you can see the uploaded file, your stage integration is configured correctly.
Note
You can also verify stage permissions by checking the stage description:
This displays the stage configuration, including the URL, credentials type, and file format settings.
On the Select tables to migrate data page, select the tables that you want to migrate.
The following image is an example of the page:
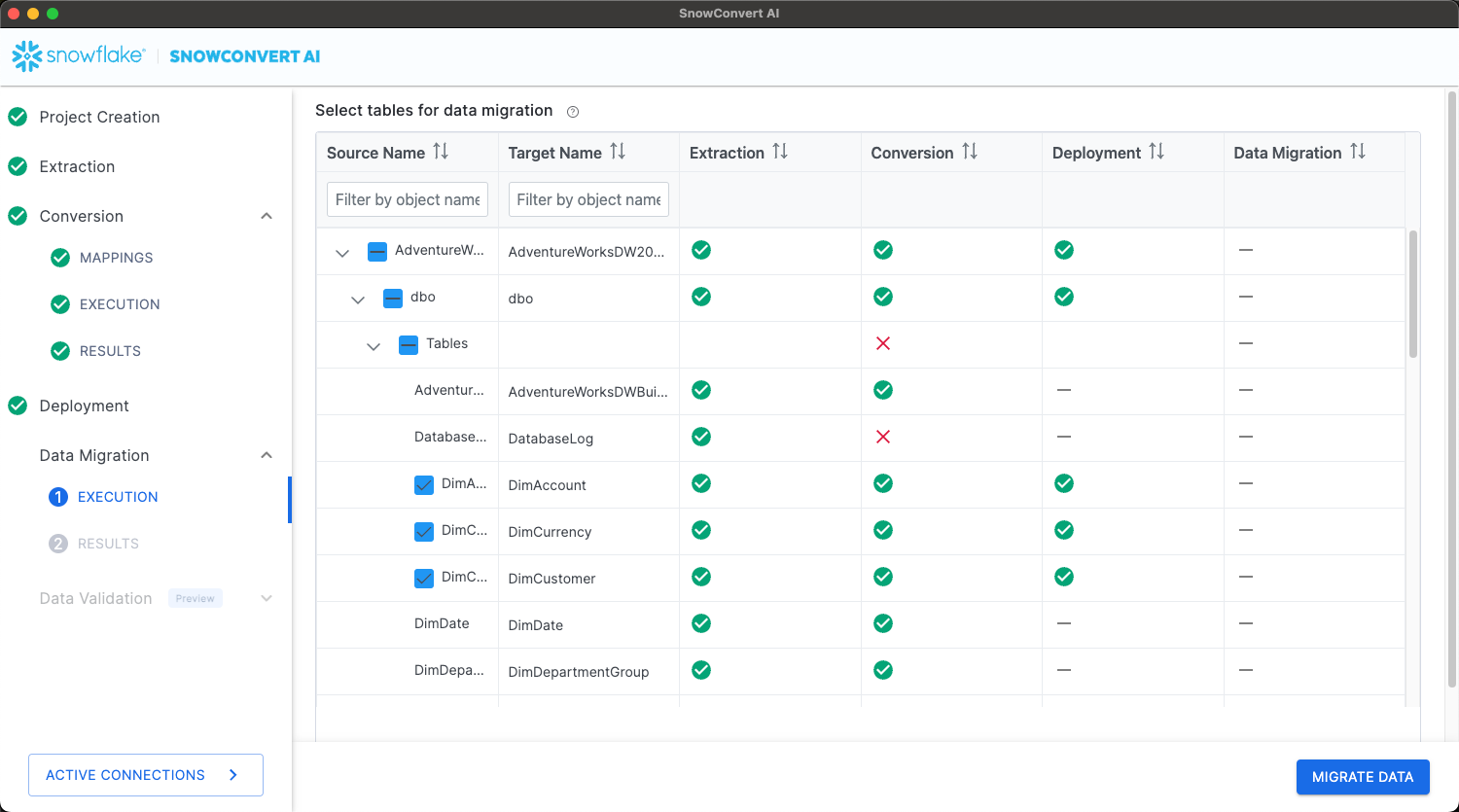
Select Migrate data.
When the migration completes successfully, the Results page appears.
If the results don’t look correct, you can select Retry data migration to run the data migration process again.
When the results look correct on the Results page, select Go to data validation to start the validation process.
Migrate SQL Server data¶
In SnowConvert AI, open the project, and then select Migrate data.
On the Connect to source database page, complete the fields with the connection information for your source database, and then select Continue.
On the Connect to Snowflake page, complete the fields with your connection information, and then select Continue.
On the Select tables to migrate data page, select the tables that you want to migrate.
The following image is an example of the page:

Select Migrate data.
When the migration completes successfully, the Results page appears.
If the results don’t look correct, you can select Retry data migration to run the data migration process again.
When the results look correct on the Results page, select Go to data validation to start the validation process.