Share secure database objects¶
Use the information provided here to share a database and its objects with one or more accounts by creating a share. You can provide a share to consumers using direct shares or listings.
You can attach a share to a listing, or convert a direct share with active consumers to a listing. For instructions, see Convert a direct share to a listing.
Are you a consumer interested in consuming shared data? See Consume imported data.
How to share database objects¶
The following are the options available for adding objects to a share:
Grant a database role to a share
Segment the securable objects in a share by creating multiple database roles in a database to a share. Grant privileges on a subset of the objects in the database to each database role. Then grant each database role to the share.
After creating a database from a share that includes database roles, data consumers grant each shared database role to one or more account roles in their own account.
Without database roles, account administrators in data consumer accounts grant a single privilege, IMPORTED PRIVILEGES, to roles to allow their users to access all databases and database objects (tables, secure views, etc.) in a share. There is no option to allow different groups of users in a data consumer account to access a subset of the shared objects. This all or nothing approach requires you to create multiple shares to grant access to different objects in the same database.
Note
If you plan to include data from multiple databases in a single share, you cannot use this option because the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege cannot be granted to a database role. For guidance sharing data from multiple databases, see Share data from multiple databases.
Alternatively, you could create a share that grants database roles to a share (Option 1), but also grants privileges on objects directly to the same share without granting privileges on those objects to a database role (Option 2). Data consumers who create databases from the share can access objects granted to the share directly by granting the IMPORTED PRIVILEGES privilege on the database to local roles.
Tip
A shared database role does not support future grants on objects. For details, see GRANT DATABASE ROLE … TO SHARE.
Grant privileges on objects directly to a share
Grants privileges on specific objects in the database directly to a share. This option allows you to include data from multiple databases in a share, as long as these databases belong to the same account. For guidance sharing data from multiple databases, see Share data from multiple databases.
Account administrators in data consumer accounts grant the IMPORTED PRIVILEGES privilege on shared databases to one or more roles to allow their users to access the databases and database objects (tables, secure views, and so on) in a share.
This option does not support segmenting database objects in a share based on roles.
Grant database roles to a share¶
This section provides instructions for data providers to restrict access to databases and database objects in a share using database roles.
Note
To perform the tasks described in this topic, your role must have the global CREATE DATABASE and CREATE SHARE privileges.
In the extended example throughout this section, a data provider shares the following objects with data consumers:
Databases |
|
|
|---|---|---|
Schemas |
|
|
Secure views |
The result set for this view includes records from table |
The result set for this view includes records from tables |
The data provider creates two database roles in database d1 to control access to these objects: d1.r1 and d1.r2.
The following diagram shows the relationships among these objects and indicates the privileges that are granted to the database roles:
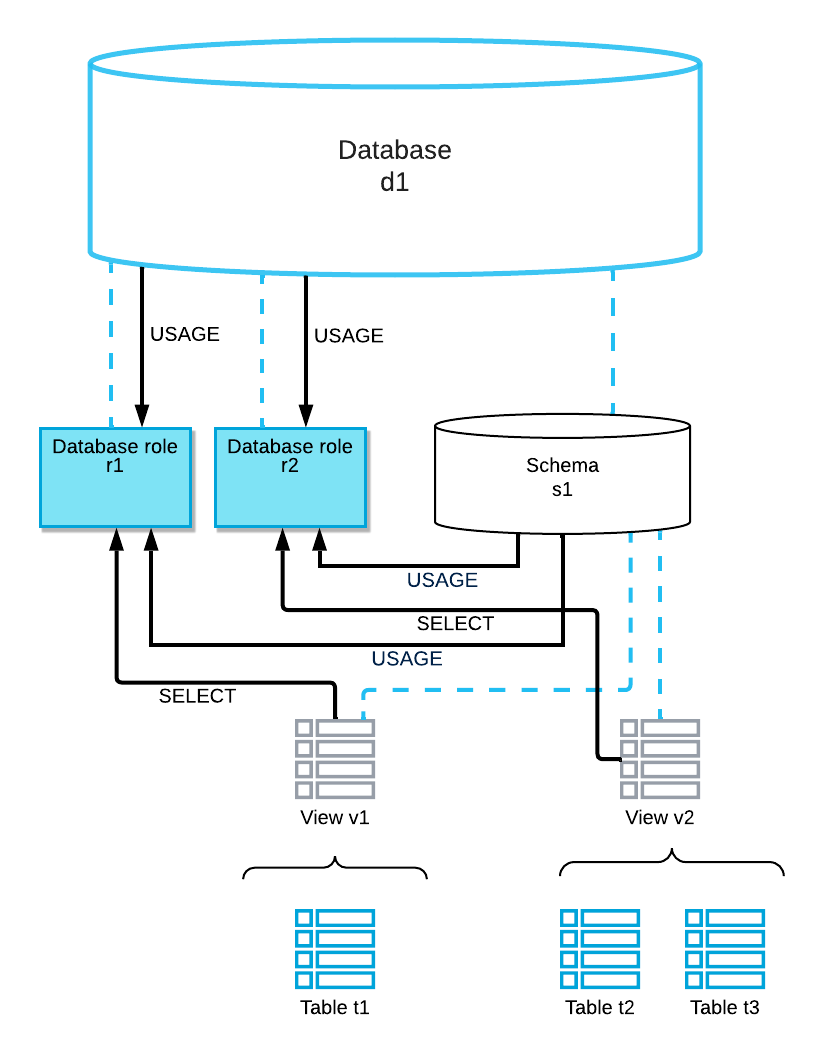
For more information about the privileges, see Access control privileges.
Create database roles¶
Create a new database role or replace an existing database role using CREATE DATABASE ROLE.
For example, create database roles d1.r1 and d1.r2 using fully-qualified identifiers:
CREATE DATABASE ROLE d1.r1;
CREATE DATABASE ROLE d1.r2;
Alternatively, set the desired database as the current database in the session, and then create the database roles:
USE DATABASE d1;
CREATE DATABASE ROLE r1;
CREATE DATABASE ROLE r2;
Grant privileges on objects to database roles¶
Grant privileges on a single database and subset of objects in the database to each database role using GRANT <privileges> … TO ROLE. Only grant privileges on objects that the database role should allow access to.
Either specify the fully-qualified name of a database role, or set the database as the active database in a session and then specify the relative name.
Note
To perform the tasks described in this topic, you must use the ACCOUNTADMIN role or a role granted the relevant privileges. For more information, including additional data sharing scenarios, see Create and configure shares.
Privileges granted to a database role are limited to USAGE on the database and schema that contain the database role and privileges on other objects in the same database. In particular, note that the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege cannot be granted to a database role to include objects from multiple databases in a share.
Continuing the extended example in these instructions, the following privileges are granted to the database roles:
Database Role |
Privilege |
Object |
|---|---|---|
|
USAGE |
Database |
USAGE |
Schema |
|
SELECT |
Secure view |
|
|
USAGE |
Database |
USAGE |
Schema |
|
SELECT |
Secure view |
The following SQL statements grant the privileges to the d1.r1 database role:
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA d1.s1 TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r1;
GRANT SELECT ON VIEW d1.s1.v1 TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r1;
The following SQL statements grant the privileges to the d1.r2 database role:
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA d1.s1 TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r2;
GRANT SELECT ON VIEW d1.s1.v2 TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r2;
Granting the USAGE privilege on the parent database is not necessary. This privilege is granted implicitly when a database role is created.
To view all privileges granted to a database role, execute SHOW GRANTS TO DATABASE ROLE using fully-qualified identifiers:
SHOW GRANTS TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r1;
SHOW GRANTS TO DATABASE ROLE d1.r2;
Alternatively, set the desired database as the current database in the session, and then execute the command:
USE DATABASE d1;
SHOW GRANTS TO DATABASE ROLE r1;
SHOW GRANTS TO DATABASE ROLE r2;
Create a share¶
Create a share using CREATE SHARE. The share is an empty container at this stage in the process.
For example, create a new share named share1:
CREATE SHARE share1;
Add the database by granting the USAGE privilege to the share¶
Currently, it is necessary to grant the USAGE privilege on a database to include it in a share.
For example, grant the USAGE privilege on the d1 database to share share1:
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE d1 TO SHARE share1;
Add objects by granting database roles to the share¶
Add databases and database objects to a share by granting database roles to the share using GRANT DATABASE ROLE … TO SHARE.
For example, grant database roles d1.r1 and d1.r2 to share share1:
GRANT DATABASE ROLE d1.r1 TO SHARE share1;
GRANT DATABASE ROLE d1.r2 TO SHARE share1;
Share the database objects with one or more data consumer accounts¶
Modify the share ALTER SHARE … ADD ACCOUNTS and add database consumer accounts with which you want to share the database objects.
The following example adds accounts consumer1 and consumer2 in organization org1 to share share1:
ALTER SHARE share1 ADD ACCOUNTS = org1.consumer1,org1.consumer2;
Manage database roles¶
This section provides instructions for managing database roles that are granted to shares.
Data providers: Renaming shared database roles¶
Rename database roles using an ALTER DATABASE ROLE … RENAME TO statement.
For example, rename database role d1.r1 to d1.r3:
ALTER DATABASE ROLE d1.r1 RENAME TO d1.r3;
All privileges granted to d1.r1 are retained after the database role is renamed.
Notify any data consumers of a share that the name of the database role has changed.
Note that moving a database role to a different database using the RENAME TO clause is prohibited. For example:
ALTER DATABASE ROLE d1.r1 RENAME TO d2.r1;
Data providers: Dropping shared database roles¶
Drop database roles using DROP DATABASE ROLE.
For example, drop database role d1.r2:
DROP DATABASE ROLE d1.r2;
Notify any data consumers of a share that includes the database role. Access to any objects granted to the database role is revoked.
Data providers: Creating new shared database roles¶
Create new database roles using CREATE DATABASE ROLE. For information, see Create database roles (in this topic). Grant privileges on database objects to a database role, and then grant the database role to a share.
Notify any data consumers of a share that includes the new database role. They must grant the new database role to their own account roles to allow those roles to access the objects associated with the database role.
Grant privileges directly to a share¶
This section provides instructions for data providers to allow consumers to access all databases and database objects in a share by granting a single privilege on shared databases.
Create a share¶
Use CREATE SHARE to create a share. At this step, the share is simply a container waiting for objects and accounts to be added.
Add objects to the share by granting privileges¶
Use GRANT <privilege> … TO SHARE to grant the following object privileges to the share:
USAGE privilege on the database you wish to share.
USAGE privilege on each database schema containing the objects you wish to share.
SELECT privilege for sharing specific objects in each shared schema:
Tables
External tables
Secure views
Secure materialized views
Secure UDFs
Important
If you plan to securely share data with data consumers across different regions or cloud platforms, note that currently, replicating a primary database is blocked if one or more external tables exist in the database.
Note
Streams cannot be shared directly. Avoid creating secure views on streams and then sharing those views with consumers. Instead, allow consumers to create their own streams on the tables and secure views that you share. For more information, see Streams on shared objects.
Optionally use SHOW GRANTS to view the object grants for the share.
Tip
Perform this minimal amount of validation of the share at this point, because after you complete the next step, the share is visible to all accounts that are added to the share.
To perform a more in-depth validation of the share, you can simulate a consumer account in your account. For more details, refer to Use secure objects to control data access.
Add one or more accounts to the share¶
Use ALTER SHARE to add one or more accounts to the share. To review the accounts added to the share, you can use SHOW GRANTS.
The share is now ready to be consumed by the specified accounts. For more detailed instructions for performing these and other data provider tasks, refer to Create and configure shares.
Example¶
The following example illustrates the entire provider process as described above.
Note that this example assumes:
A database named
sales_dbexists with a schema namedaggregates_eulaand a table namedaggregate_1.The database, schema, and table will be shared with two accounts named
xy12345andyz23456.USE ROLE accountadmin; CREATE SHARE sales_s; GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE sales_db TO SHARE sales_s; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA sales_db.aggregates_eula TO SHARE sales_s; GRANT SELECT ON TABLE sales_db.aggregates_eula.aggregate_1 TO SHARE sales_s; SHOW GRANTS TO SHARE sales_s; ALTER SHARE sales_s ADD ACCOUNTS=xy12345, yz23456; SHOW GRANTS OF SHARE sales_s;Copy