Manage reader accounts¶
Reader accounts (formerly known as “read-only accounts”) enable providers to share data with consumers who are not already Snowflake customers, without requiring the consumers to become Snowflake customers.
Note
All tasks described in this topic must be performed using the ACCOUNTADMIN role or a role granted the CREATE ACCOUNT global privilege.
Overview¶
A reader account enables data consumers to access and query data shared by the provider of the account, with no setup or usage costs for the consumer, and no requirements for the consumer to sign a licensing agreement with Snowflake.
The reader account is created, owned, and managed by the provider account, which assumes all responsibility for credit charges incurred by users in the reader account. Similar to standard consumer accounts, the provider account uses shares to share databases with reader accounts; however, a reader account can only consume data from the provider account that created it.
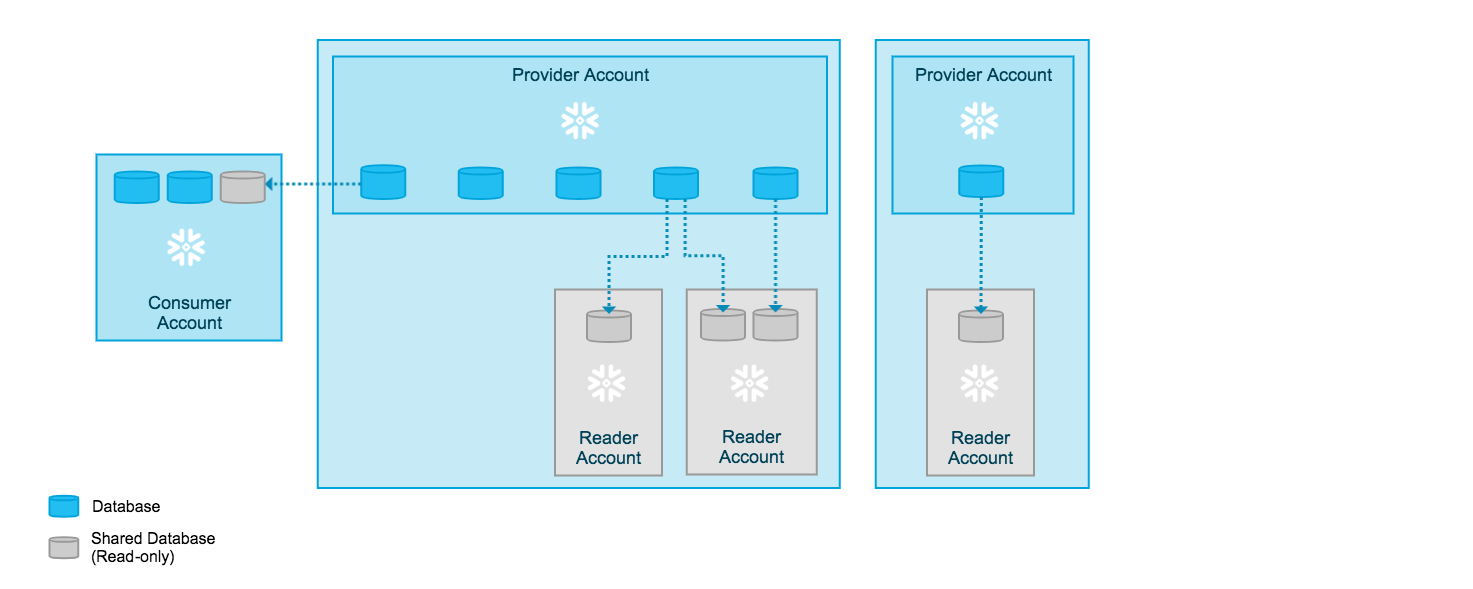
Note
Warehouses in a reader account can consume an unlimited number of credits each month, which will be charged to your provider account. To limit usage, set up a resource monitor for the warehouse.
What is restricted/allowed in a reader account?¶
A reader account is intended primarily for querying data shared by the provider of the account. You can work with data, for example, by creating materialized views.
You cannot perform the following tasks in a reader account:
Set a data metric function on objects in the reader account.
Upload new data.
Modify existing data.
Unload data using a storage integration. However, you can use the COPY INTO <location> command with your connection credentials to unload data into a cloud storage location.
Additionally, you cannot execute the following commands in a reader account:
All other operations are allowed.
Who provides support for a reader account?¶
Because a reader account does not have a licensing agreement with Snowflake, support services are not available to the general users in the account. Instead, as the provider of the account, you field questions and requests from users in the account and respond as appropriate.
If you are unable to directly answer their questions or resolve their requests/issues, you can open a Snowflake Support ticket through the normal channels (as outlined in your support agreement). Once a response has been provided by Snowflake Support, you then communicate the information back to the appropriate users in the reader account.
Managing and creating reader accounts using the web interface¶
If you have the ACCOUNTADMIN role (or have a role that has been granted the CREATE ACCOUNT privilege), you can use Snowsight to perform most tasks related to creating and managing reader accounts.
Using Snowsight¶
To create or manage reader accounts in Snowsight, do the following:
Sign in to Snowsight.
In the navigation menu, select Admin » Accounts.
Select the Accounts tab.
Select the Reader accounts sub-tab.
On this page, you can do the following:
Create a reader account by selecting + New.
Review existing reader accounts.
Drop a reader account by selecting … » Drop.
Note
By default, the total number of reader accounts a provider can create is 20. If you reach the limit and require creating additional accounts, please contact Snowflake Support.
If you dropped a reader account in order to create a new account without exceeding this limit, you cannot create the new reader account for 7 days, which is the retention period for deleted reader accounts.
DDL for reader accounts¶
To enable creating and managing reader accounts, Snowflake provides a first-class object, MANAGED ACCOUNT, that supports the following DDL commands:
Enabling other roles to create and manage reader accounts¶
By default, only users with the ACCOUNTADMIN role can create reader accounts and therefore, as the owner of the account, manage the accounts. To support delegating these tasks to other users, the CREATE ACCOUNT global privilege can be granted to other roles (system-defined or custom). Then, users with the role can create reader accounts and perform all tasks associated with managing the accounts created using the role.
For example, to grant the privilege to the SYSADMIN role:
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN; GRANT CREATE ACCOUNT ON ACCOUNT TO ROLE SYSADMIN;
Creating and managing reader accounts using SQL¶
In addition to using the web interface to manage and create reader accounts, you can also use SQL.
Creating a reader account¶
To create a reader account, use the ACCOUNTADMIN role (or a role granted the CREATE ACCOUNT global privilege) and the CREATE MANAGED ACCOUNT command.
In the command, specify the identifier for the account and the user who will serve as the administrator for the account. For example, use the following syntax:
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN;
CREATE MANAGED ACCOUNT <account_name>
ADMIN_NAME = <username> , ADMIN_PASSWORD = '<password>' ,
TYPE = READER;
After running the command, you see the account name and login URL for the account:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| status |
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| {"accountName":"READER_ACCT1","accountLocator":"IIB88126","url":"https://myorg-reader_acct1.snowflakecomputing.com","accountLocatorUrl":"https://iib88126.snowflakecomputing.com"}|
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Note:
By default, the total number of reader accounts a provider can create is 20. If you reach the limit and require creating additional accounts, please contact Snowflake Support.
If you dropped a reader account in order to create a new account without exceeding this limit, you cannot create the new reader account for 7 days, which is the retention period for deleted reader accounts.
The
urlis the preferred account URL for the new reader account. The account locator is a legacy identifier for the account.The reader account utilizes the same Snowflake Edition as the provider account and is created in the same region.
Important
After creating a reader account, wait for up to five minutes to ensure that the account is fully provisioned. Then, you must perform the following additional tasks before the account is ready to use:
Add the account to one or more shares so that the Snowflake objects in the shares can be shared with the account.
Renaming a reader account¶
You must use SQL commands to rename a reader account. For instructions, see Renaming an account.
Dropping a reader account¶
To drop a reader account, use the DROP MANAGED ACCOUNT command. For example:
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN; DROP MANAGED ACCOUNT reader_acct1;
Attention
Dropping a reader account drops all the objects created in the account and immediately restricts all access to the account. It also removes the account from your total number of reader accounts.
This operation can not be undone. Before you drop a reader account, please take this into consideration.
Viewing reader accounts¶
To view all the reader accounts that have been created for your account, use the SHOW MANAGED ACCOUNTS command. For example:
USE ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN; SHOW MANAGED ACCOUNTS;
This command can be used to monitor the total number of reader accounts for your account. If the total number reaches the limit (20), you may need to drop some accounts or contact Snowflake Support to request the limit be increased.
In addition, you can use the views in the READER_ACCOUNT_USAGE schema (in the SNOWFLAKE shared database) to query information about the reader accounts created for your account. For more details, see Account Usage.
Redirecting client connections in case of failover¶
In the event of an outage in a region, you can use Client Redirect to provide continued access to data consumers using reader accounts. Create two reader accounts in different regions and designate one to act as the primary connection. In the event of an outage in a region, you can redirect client connections to the reader account in another region. For more information, see Configuring Client Redirect and reader accounts.