SnowConvert AI - SQL Server¶
The first step for migration is getting the code that you need to migrate. There are many ways to extract the code from your database. However, we highly recommend using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), nevertheless we provide an alternative for MacOS and Linux environments.
Prerequisites¶
Access to a server with an SQLServer database.
Extraction Via SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)¶
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is only available for Windows. Go to the next section for Mac OS and Linux.
Open SSMS.
Connect to the desired server and server instance with credentials that allow visibility of the desired database(s).
In the main SSMS window, open Object Explorer if not already opened.
In the Object Explorer pane, expand Databases if not already expanded.
Right-click on the desired database and select Tasks -> Generate Scripts…
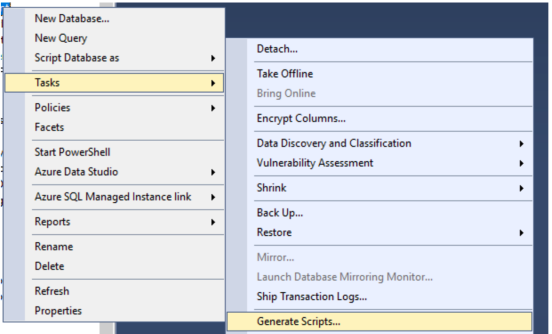
If the Introduction page of the Generate Scripts dialog is shown, click Next. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
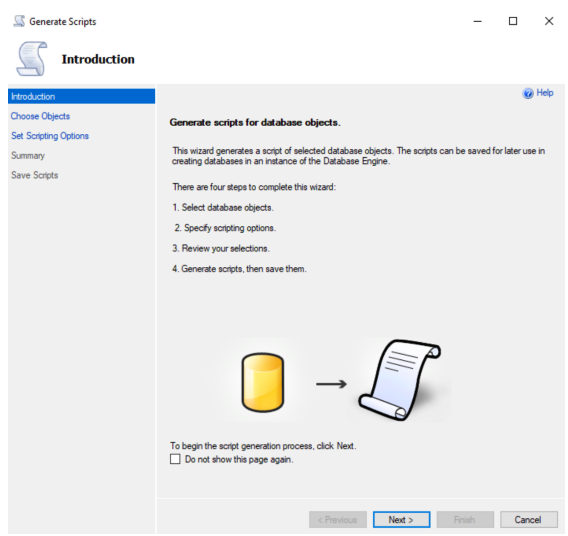
On the Choose Objects page of the Generate Scripts dialog:
Select the Select specific database objects radio button and put a check in all the database object type checkboxes displayed EXCEPT Users (NOTE: the list of database object types presented depends on the presence of database objects in the chosen database. Thus, your list of database object types may look different. Just select all database object types EXCEPT Users).
Click Next
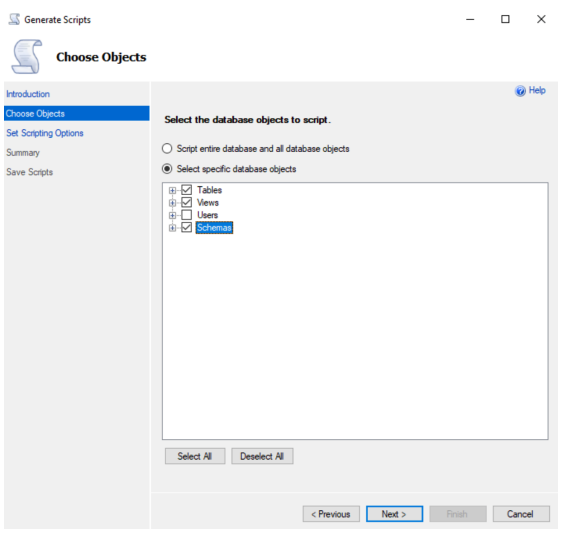
On the Set Scripting Options page of the Generate Scripts dialog:
Click the Save as script file button and One script file per object
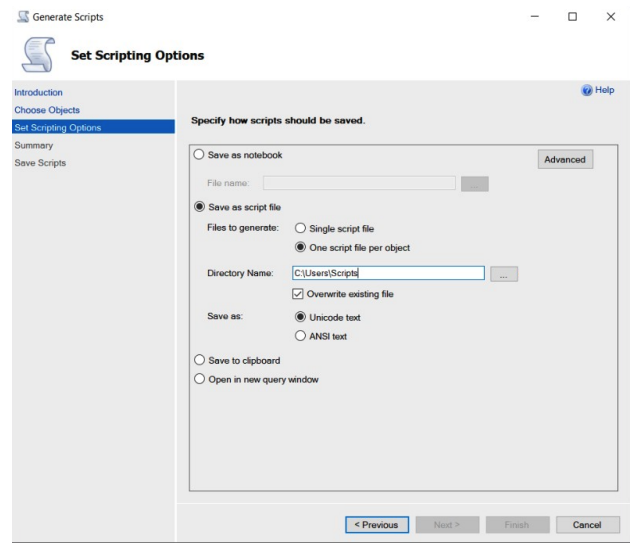
Click the Advanced button.
In the Advanced Scripting Options dialog box, make sure the following Options are set as indicated, keeping the default for all other Option
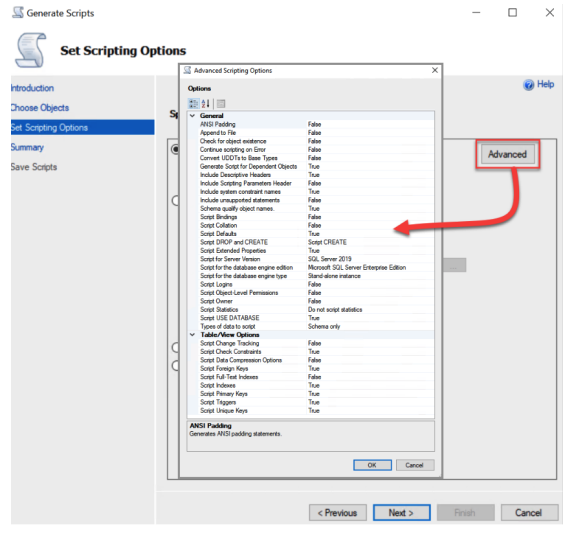
Section |
Setting. |
Value |
|---|---|---|
General |
Include System Constraint names |
True |
empty |
Script Extended Properties |
True |
Table/View Options |
Script Indexes |
True |
- |
Script Triggers |
True |
When done, click OK to return to the Set Scripting Options window of the Generate Scripts dialog.
Select the Save as script file radio button.
Click the ellipsis (…) to the right of the File name: field.
Navigate to a suitable location, enter a descriptive value (e.g.,<server_name>_<instance_name>_<database_name>) in the File Name: field, and click Save.
Select the ANSI text radio button.
Click Next.
On the Summary page of the Generate Scripts dialog, confirm the settings are correct and click Next > when ready to start the extraction (i.e., the extraction will commence when you click Next >). The Save Scripts page will appear and will show the extraction progress.
On the Save Scripts page of the Generate Scripts dialog box (not shown), confirm all Results were Success and click Finish.
Repeat steps 5 through 10 for each desired database (using a different file name for each). When all databases have been extracted successfully, proceed to the next step.
Transmit the resulting file(s) to Snowflake for further analysis.
Package the results¶
When the extraction process is finished, compress the results and send them over.
Table sizing report¶
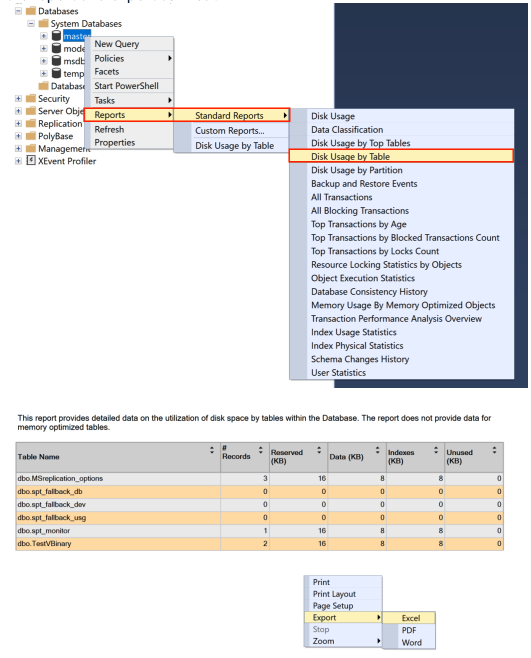
Option A: For all databases in scope, right click on the database, Reports > Standard Reports > Disk Usage By Table. A report will be generated, right click on the report and export as Excel.
Option B: Run the following script:
USE <DB_NAME>;
SELECT
t.NAME AS TableName,
s.NAME AS SchemaName,
SUM(a.total_pages) * 8 / 1024 AS TotalSpaceMB,
SUM(a.used_pages) * 8 / 1024 AS UsedSpaceMB,
(SUM(a.total_pages) - SUM(a.used_pages)) * 8 / 1024 AS
UnusedSpaceMB
FROM
sys.tables t
INNER JOIN
sys.indexes i ON t.OBJECT_ID = i.object_id
INNER JOIN
sys.partitions p ON i.object_id = p.OBJECT_ID AND i.index_id =
p.index_id
INNER JOIN
sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN
sys.schemas s ON t.schema_id = s.schema_id
GROUP BY
t.NAME, s.NAME, p.Rows
ORDER BY
TotalSpaceMB DESC;