About Secure Data Sharing¶
Secure Data Sharing lets you share selected objects in a database in your account with other Snowflake accounts. You can share the following Snowflake objects:
Databases
Tables
Dynamic tables
External tables
Externally managed and managed Apache Iceberg™ tables
Externally managed Delta Lake tables (with Delta Direct and catalog-linked databases)
Views
Regular views
Secure views
Secure materialized views
Semantic views
Cortex Search services
User-defined functions (UDFs) (secure and non-secure)
Models of type USER_MODEL, CORTEX_FINETUNED, or DOC_AI
Snowflake enables the sharing of databases through shares, which are created by data providers and “imported” by data consumers.
Important
All database objects shared between accounts are read-only (i.e. the objects cannot be modified or deleted, including adding or modifying table data).
How does Secure Data Sharing work?¶
With Secure Data Sharing, no actual data is copied or transferred between accounts. All sharing uses Snowflake’s services layer and metadata store. Shared data does not take up any storage in a consumer account and therefore does not contribute to the consumer’s monthly data storage charges. The only charges to consumers are for the compute resources (i.e. virtual warehouses) used to query the imported data.
Because no data is copied or exchanged, Secure Data Sharing setup is quick and easy for providers and access to the imported data is near-instantaneous for consumers:
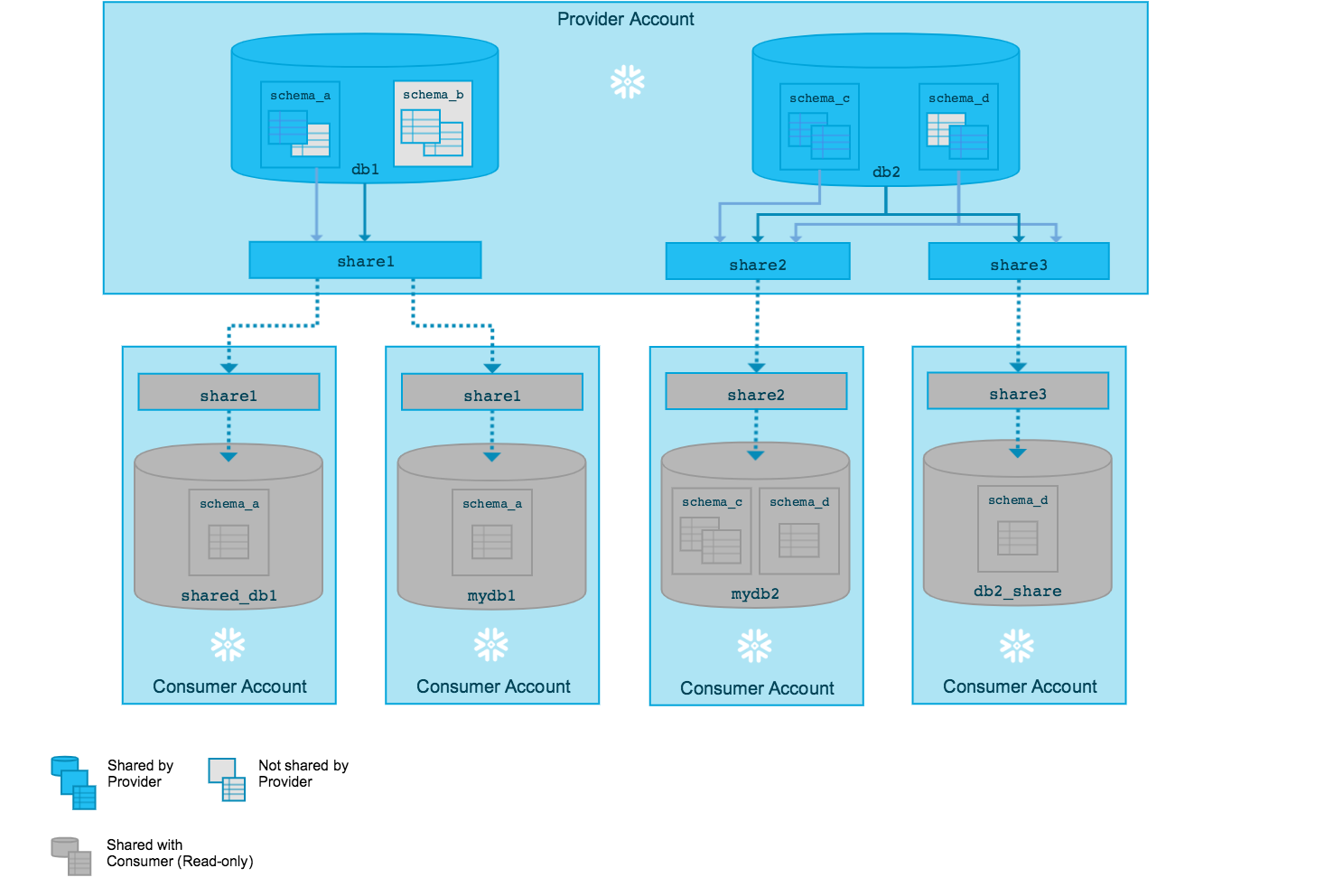
The provider creates a share of a database in their account and grants access to specific objects in the database. The provider can also share data from multiple databases, as long as these databases belong to the same account. One or more accounts are then added to the share, which can include your own accounts (if you have multiple Snowflake accounts).
For more details, refer to What is a share? (in this topic).
On the consumer side, a read-only database is created from the share. Access to this database is configurable using the same, standard role-based access control that Snowflake provides for all objects in the system.
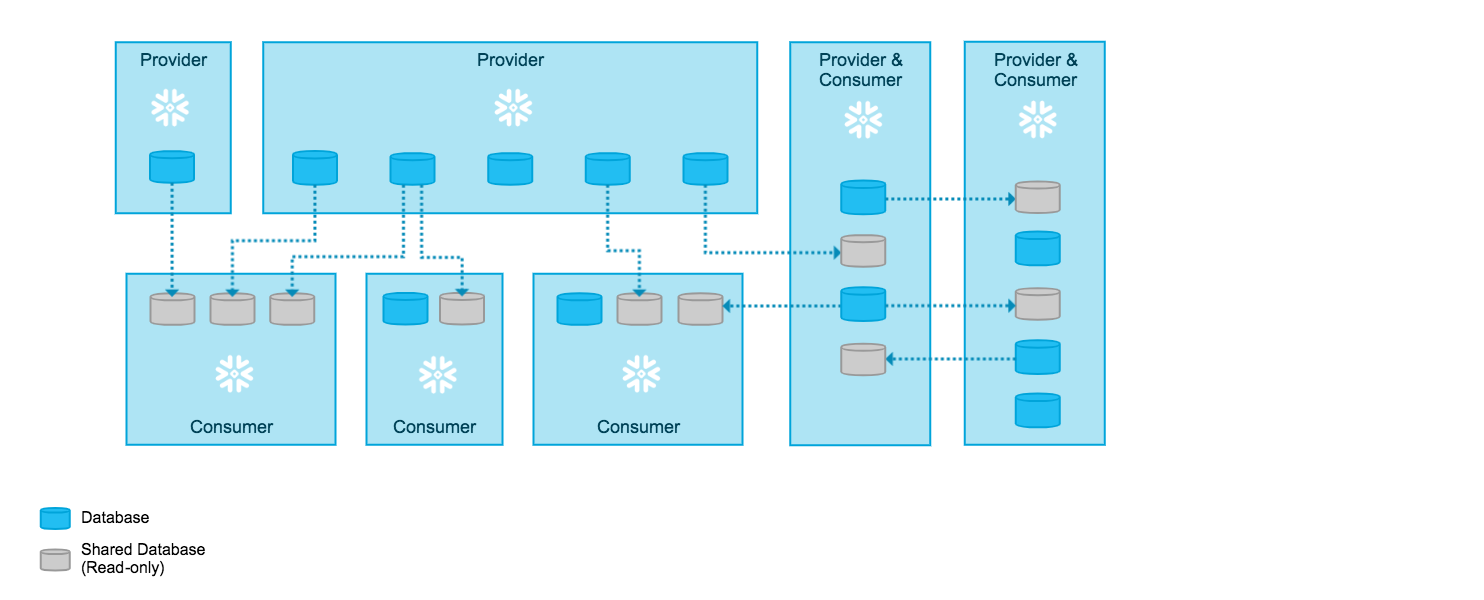
With this architecture, Snowflake enables a network of providers that can share data with multiple consumers (including within their own organization) and consumers that can access imported data from multiple providers:
Note
Any full Snowflake account can both provide and consume imported data. Snowflake also supports third-party accounts, a special type of account that consumes imported data from a single provider account. For more details, refer to Reader accounts for third-party access (in this topic).
Options for sharing in Snowflake¶
You can share data in Snowflake using one of the following options:
a Listing, in which you offer a share and additional metadata as a data product to one or more accounts,
a Direct Share, in which you directly share specific database objects (a share) to another account in your region,
a Data Exchange, in which you set up and manage a group of accounts and offer a share to that group,
a clean room, in which you can share data and control which queries can be run against our data.
You can also convert a direct share to a listing. For instructions, see Convert a direct share to a listing.
See Data sharing and collaboration in Snowflake for more details.
Overview of data providers and consumers¶
When sharing in Snowflake, the account that shares data is called a provider, and the account that is a recipient of the data is called a consumer.
About providers¶
A data provider is any Snowflake account that creates shares and makes them available to other Snowflake accounts to consume. As a data provider, you share a database with one or more Snowflake accounts. For each database you share, Snowflake supports using grants to provide granular access control to selected objects in the database (i.e., you grant access privileges for one or more specific objects in the database).
You can create as many shares as you want, and add as many accounts to a share as you want. If you want to provide a share to many accounts, you might want to use a listing or a data exchange.
For a guide to sharing data as a provider, refer to Share secure database objects. For more detailed information, refer to Create and configure shares.
About consumers¶
A data consumer is any account that chooses to create a database from a share made available by a data provider. As a data consumer, once you add an imported database to your account, you can access and query the objects in the database just as you would with any other database in your account.
You can consume as many shares as you want from data providers, but you can only create one database per share.
For more details, refer to Consume imported data.
Reader accounts for third-party access¶
Data sharing is only supported between Snowflake accounts. As a data provider, you might want to share data with a consumer who does not already have a Snowflake account or is not ready to become a licensed Snowflake customer.
To facilitate sharing data with these consumers, you can create reader accounts. Reader accounts (formerly known as “read-only accounts”) provide a quick, easy, and cost-effective way to share data without requiring the consumer to become a Snowflake customer.
Each reader account belongs to the provider account that created it. As a provider, you use shares to share databases with reader accounts; however, a reader account can only consume data from the provider account that created it. Refer to the following diagram:
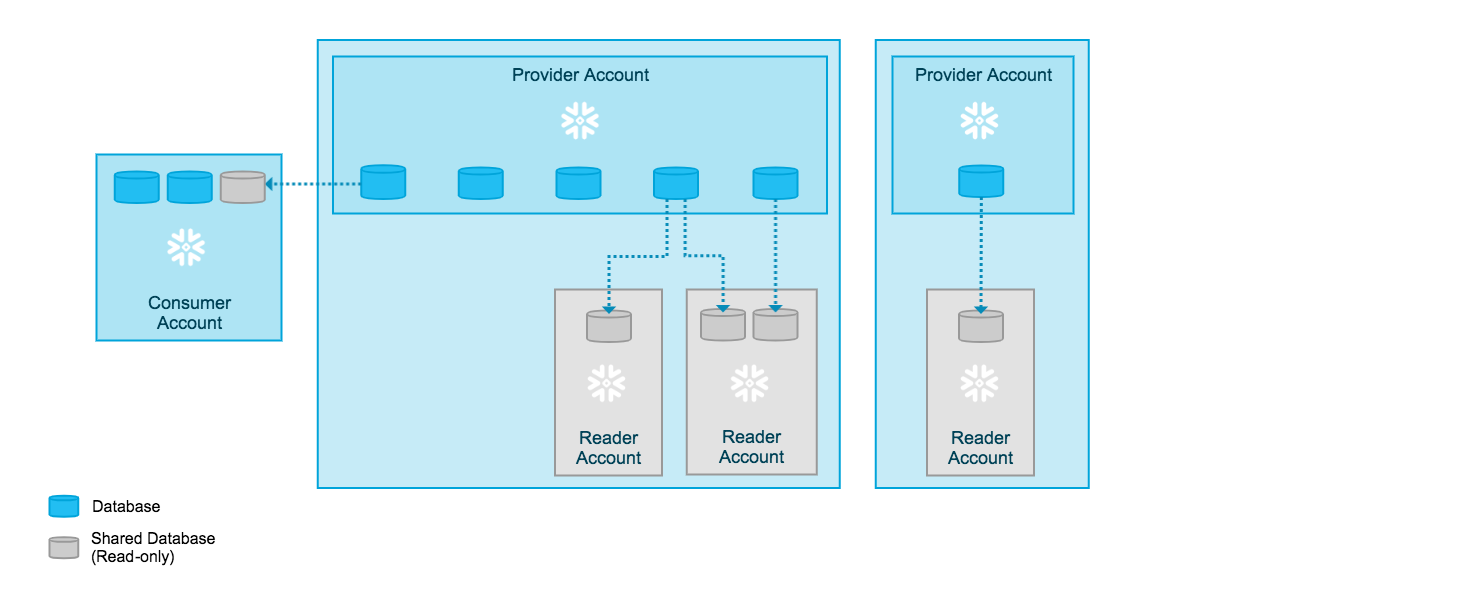
Users in a reader account can query data that has been imported with the reader account, but cannot perform any of the DML tasks that are allowed in a full account, such as data loading, insert, update, and similar data manipulation operations.
For more details, refer to Manage reader accounts.