Share data from multiple databases¶
Snowflake data providers can share data from multiple databases by using secure views. A secure view can reference objects such as schemas, tables, and other views contained in one or more databases, as long as those databases belong to the same account.
Sharing a secure view that references objects from multiple databases is different from sharing data contained in a single database.
In addition to performing all the standard steps to share data, you must also grant the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege on each database referenced by a secure view that you wish to share. However, you do not need to grant REFERENCE_USAGE on the database that contains the secure view.
Note
You cannot use database roles to share data from multiple databases. You cannot grant the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege to a database role and you cannot use a database role to grant a secure view that references objects from multiple databases to a share.
You must grant the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege separately on each database referenced in a secure view, before granting the secure view to a share.
To share a secure view that references objects from multiple databases:
Connect to your Snowflake account as a user with the ACCOUNTADMIN role or a role granted the CREATE SHARE global privilege. For more details about the CREATE SHARE privilege, see Enable non-ACCOUNTADMIN roles to perform data sharing tasks.
Create a share using CREATE SHARE.
Grant the USAGE privilege on the database you wish to share using GRANT <privilege> … TO SHARE.
Note
If you are sharing a secure view that references objects contained in multiple databases, you only need to grant the USAGE privilege to the database where the secure view is created. You can only grant USAGE to one database per share.
Granting the USAGE privilege to the database associates the share with a database, which is required to grant other privileges to the share.
Grant the USAGE privilege on each schema in the database you wish to share using GRANT <privilege> … TO SHARE.
Grant the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege on each additional database that contains objects referenced by the view you wish to share using GRANT <privilege> … TO SHARE.
Add the view to the share by granting the SELECT privilege on the view using GRANT <privilege> … TO SHARE.
Add one or more consumer accounts to the share using ALTER SHARE.
The share is now ready to be consumed by the specified accounts.
Note
To share a secure view that references a UDF in a different database, you must make the UDF secure. For more details about creating a secure UDF, see Creating a Secure UDF or Stored Procedure.
Examples¶
Refer to the following examples for creating secure views.
Example 1: Create and share a secure view in an existing database¶
A provider who organizes data into different databases based on the characteristics of data and business needs wants to share a secure view in one database that joins data in the database with objects (e.g. schema, table, view) in other databases.
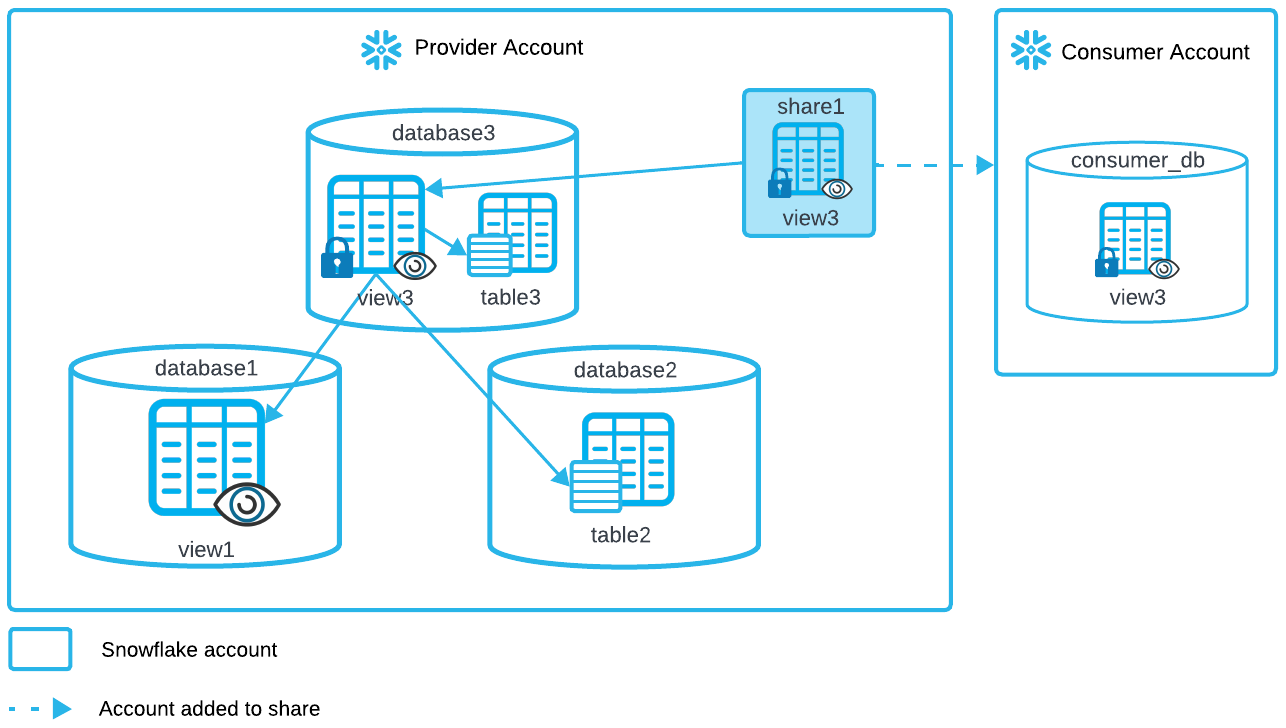
Create database
database1and data:CREATE DATABASE database1; CREATE SCHEMA database1.sch; CREATE TABLE database1.sch.table1 (id INT); CREATE VIEW database1.sch.view1 AS SELECT * FROM database1.sch.table1;
Create database
database2and data:CREATE DATABASE database2; CREATE SCHEMA database2.sch; CREATE TABLE database2.sch.table2 (id INT);
Create database
database3and data:CREATE DATABASE database3; CREATE SCHEMA database3.sch; CREATE TABLE database3.sch.table3 (id INT);
Create the secure view with the data to be shared in
database3:CREATE SECURE VIEW database3.sch.view3 AS SELECT view1.id AS View1Id, table2.id AS table2id, table3.id AS table3id FROM database1.sch.view1 view1, database2.sch.table2 table2, database3.sch.table3 table3;
Create the share and grant required privileges to set up the share.
CREATE SHARE share1; GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE database3 TO SHARE share1; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA database3.sch TO SHARE share1;
Grant the required privileges necessary to add the secure view
view3to the share.The data referenced in additional databases by secure view
view3requires granting the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege ondatabase1anddatabase2to the share:GRANT REFERENCE_USAGE ON DATABASE database1 TO SHARE share1; GRANT REFERENCE_USAGE ON DATABASE database2 TO SHARE share1; GRANT SELECT ON VIEW database3.sch.view3 TO SHARE share1;
You can share this data with consumers in other regions by using a replication group to replicate data to an account in another region. For instructions, see Example 3: Share data from multiple databases.
Example 2: Create and share a secure view in a separate database¶
A provider stores customer data in separate databases and does not want to create new objects in those databases. To share data, the provider creates a new database with a secure view. The secure view references objects (schema, table, view) in the databases with customer data.
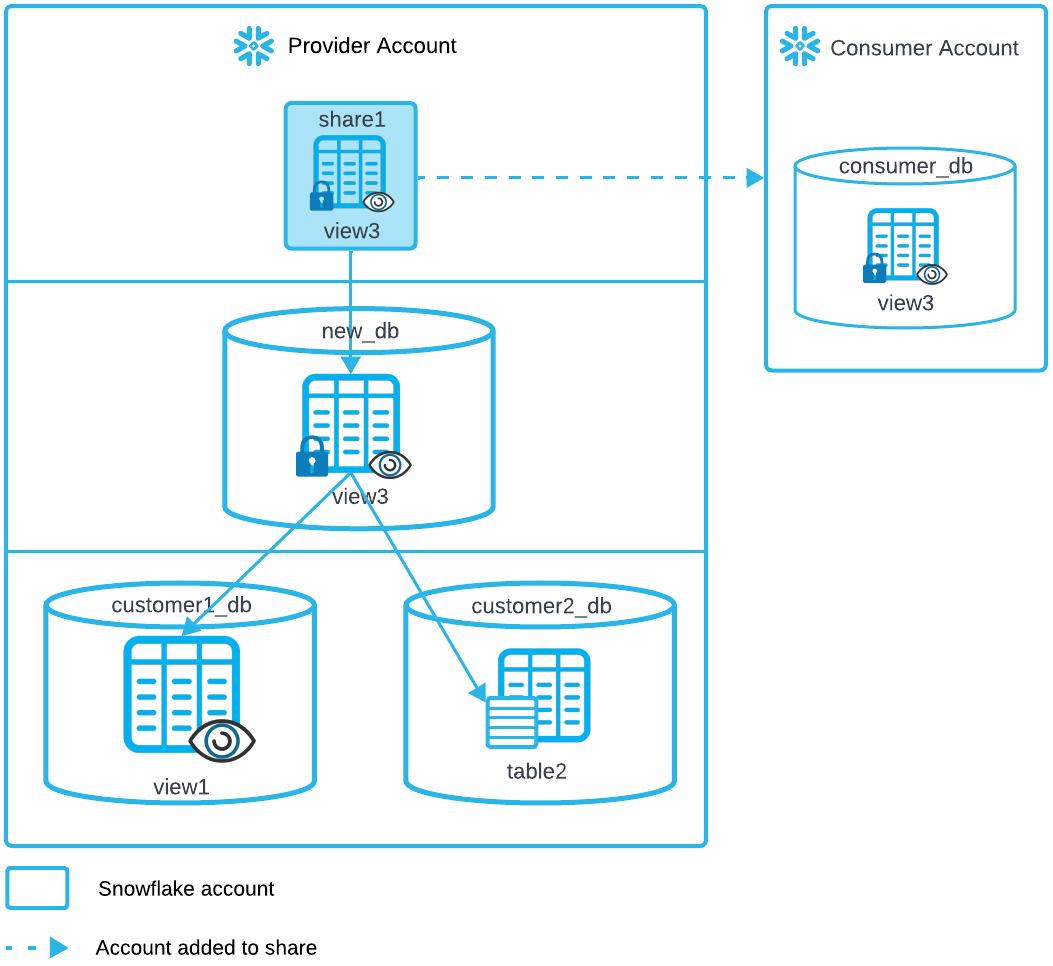
Sample Code:
Create the customer database
customer1_dband data:CREATE DATABASE customer1_db; CREATE SCHEMA customer1_db.sch; CREATE TABLE customer1_db.sch.table1 (id INT); CREATE VIEW customer1_db.sch.view1 AS SELECT * FROM customer1_db.sch.table1;
Create the customer database
customer2_dband data:CREATE DATABASE customer2_db; CREATE SCHEMA customer2_db.sch; CREATE TABLE customer2_db.sch.table2 (id INT);
Create the new database
new_dband schemasch:CREATE DATABASE new_db; CREATE SCHEMA new_db.sch;
Create the secure view in
new_dbthat references objects incustomer1_dbandcustomer2_db:CREATE SECURE VIEW new_db.sch.view3 AS SELECT view1.id AS view1Id, table2.id AS table2ID FROM customer1_db.sch.view1 view1, customer2_db.sch.table2 table2;
Create the share and grant required privileges to set up the share:
CREATE SHARE share1; GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE new_db TO SHARE share1; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA new_db.sch TO SHARE share1;
Grant the required privileges necessary to add the secure view
view3to the share.The data referenced in additional databases by secure view
view3requires granting the REFERENCE_USAGE privilege oncustomer1_dbandcustomer2_dbto the share:GRANT REFERENCE_USAGE ON DATABASE customer1_db TO SHARE share1; GRANT REFERENCE_USAGE ON DATABASE customer2_db TO SHARE share1; GRANT SELECT ON VIEW new_db.sch.view3 TO SHARE share1;
Sharing data from multiple database with consumers in other regions¶
You can share data from multiple databases with consumer accounts in other regions and cloud platforms by using a replication group. Include the share and each database the share references in the group to replicate data to a Snowflake account in another region. You can then add consumer accounts to the replicated share. For detailed instructions, see Share data securely across regions and cloud platforms.